Math - Collision
[TOC]
충돌 판정에 사용하는 형태
| 형태 | 특징 | 구조체 |
|---|---|---|
| 선분 | - 좌표 2개를 이은 선 - 굵기가 없는 선 형태 |
시작점, 벡터 |
| 구 | - 중심에서 같은 거리에 있는 면으로 만든 형태 - 중심과 반지름으로 표현 |
중심좌표, 반지름 |
| 평면 (삼각형) |
- 3차원 공간에 무한히 퍼져 있는 평평한 면 - 평면 방정식으로 표현 - 삼각형일 때는 평면을 범위로 제한 |
- 평면의 성분 - 꼭짓점 3개, 삼각형을 포함하는 평면(계산 편의) |
충돌 대상별 특징
| 대상1 | 대상2 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| 직선 | 직선 | 직선끼리의 충돌은 근본적으로 y에 수직인 직선을 정의할 수 없으므로 y에 수직인 직선과의 교점을 찾을 수 없다. - y에 수직인 직선은 기울기가 a/0이기 때문 이를 위해 직선의 매개변수를 이용한 방정식을 사용해야하는데 이러면 순수한 직선은 아니다. |
| 선분 | 선분 | 공식의 유도 과정에서 연립방정식을 풀기위해 행렬, 역행렬, 행렬식을 사용해서 어렵다. 공식을 구한 뒤 사용은 어렵진 않다. 2차원에서 사용하고 3차원에서는 거의 충돌하지 않으므로 사용하지 않는다. 공식의 유도가 복잡하다. |
| 선분 | 구 | 직선의 매개변수 방정식과 근의 공식을 사용한다. 복잡하다. |
| 선분 | 평면 | 평면의 방정식과 직선의 매개변수 방정식을 사용한다. |
| 선분 | 삼각형 | 선분과 평면의 충돌 검사를 하고 추가로 선분이 삼각형 내부에 있는지 검사해야한다. 방법은 선분과 삼각형을 포함하는 평면의 접점과 각 꼭지점을 연결한 벡터를 구하고 이 벡터와 변의 외적 벡터를 구해 모두 같은 방향이면 내부, 하나라도 다른 방향이면 외부에 있다고 판단한다. 복잡하다 |
| 구 | 구 | 중심점의 거리만 계산하면 되므로 편리하다. |
| 구 | 평면 | 평면과 구의 중심점의 거리만 계산하므로 편리하다. |
| 구 | 삼각형 | 1. 평면과 구의 거리 계산 2. 삼각형 각 선분과 구의 충돌을 검사 - 구와 선분의 충돌 이용 3. 구의 중심에서 삼각형을 포함한 평면에 내린 수선과 평면의 교점이 삼각형 내부에 있는지 검사 - 선분과 삼각형의 충돌 이용 복잡하다. |
| 평면 | 평면 | 평면끼리는 평면의 법선 벡터끼리 외적하여 교선의 벡터는 간단하게 구할 수 있다. 추가로 교선의 시작점을 찾기위해서는 좌표의 요소중 하나를 0으로 가정하여 두 평면의 방정식을 연립하여 풀면된다. 이 때 교선의 벡터의 성분중 0인 성분이 있다면 다른 성분을 0으로 가정해야한다. 시작점 찾기는 복잡하다. |
| 평면 | 삼각형 | 평면과 삼각형은 삼각형의 각 꼭지점들이 평면의 위와 아래에 분포돼있으면 충돌했다고 판단한다. 간단하다. |
| 삼각형 | 삼각형 | 삼각형과 삼각형은 삼각형의 각 선분이 다른 삼각형의 내부에 있는지 판단하면 된다. 선분과 삼각형의 충돌을 이용하면 되고 비용이 많이 든다. 복잡하다. |
직선과 한 점의 거리
Todo
직선과 직선의 충돌
직선의 방정식 - 기울기와 y절편이 주어졌을 때
\[a:기울기, b:y절편 \\ y = ax + b\]직선의 방정식 - 기울기와 한 점의 좌표가 주어졌을 때
\[a:기울기, P:한 점 \\ P_y = aP_x + b \\ P_y - aP_x = b \\ \therefore b = P_y - aP_x \\ \text{b를 대입} \\ y = ax + P_y - aP_x \\ \therefore y - P_y = a(x - p_x)\]직선의 방정식 - 두 점이 주어졌을 때
\[P:한 점, Q:두 점 \\ \text{'기울기와 한 점의 좌표' 공식에 대입} \\ y - P_y = \frac{Q_y - P_y}{Q_x - P_x}(x - p_x) \\ Q_y = P_y\text{라면 기울기가 0이되어 x축에 평행인 } y = P_y 직선이 되고 \\ Q_x = P_x\text{라면 기울기를 구할 수 없기 때문에 } x = P_x 직선이 된다. \\ \text{그 외는 위 식을 전개하면 된다.}\]직선의 충돌 이론
직선이 충돌한다는 것은 교점이 있다는 것
두 직선의 방정식을 연립하여 해를 구하면 된다.
해가 없다. -> 교점이 없다. 충돌(교차)하지 않는다.
해가 무수히 많다. -> 두 직선이 겹친다. 기울기와 y절편이 같다. 충돌(교차)하지 않는다.
해가 하나이다. -> 교점이 있다. 충돌(교차)한다.
\[P:시작점, a:기울기 \\ y = a_1(x-p_{1x})+p_{1y} \\ y = a_2(x-p_{2x})+p_{2y} \\\] \[\text{y에 대입}\\\\ a_1(x-p_{1x})+p_{1y} = a_2(x-p_{2x})+p_{2y} \\ a_1x-a_1p_{1x}+p_{1y} = a_2x-a_2p_{2x}+p_{2y} \\ a_1x-a_2x = -a_2p_{2x}+p_{2y}+a_1p_{1x}-p_{1y} \\ \therefore x = \frac{-a_2p_{2x}+p_{2y}+a_1p_{1x}-p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2} \\\] \[\require{cancel} \text{x에 대입}\\\\ y = a_1x-a_1p_{1x}+p_{1y}\\ y = a_1(\frac{-a_2p_{2x}+p_{2y}+a_1p_{1x}-p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2})-a_1p_{1x}+p_{1y} \\ y = \frac{-a_1a_2p_{2x}+a_1p_{2y}+a_1^2p_{1x}-a_1p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2}-a_1p_{1x}+p_{1y} \\ y = \frac{-a_1a_2p_{2x}+a_1p_{2y}+a_1^2p_{1x}-a_1p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2} - \frac{a_1^2p_{1x}-a_1a_2p_{1x}}{a_1-a_2} + \frac{a_1p_{1y}-a_2p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2} \\ y = \frac{-a_1a_2p_{2x}+a_1p_{2y}+\cancel{a_1^2p_{1x}}-\cancel{a_1p_{1y}} - \cancel{a_1^2p_{1x}} + a_1a_2p_{1x} + \cancel{a_1p_{1y}}-a_2p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2} \\ \therefore y = \frac{-a_1a_2p_{2x}+a_1p_{2y} + a_1a_2p_{1x} - a_2p_{1y}}{a_1-a_2}\]직선의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Line_Line_Collision : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform LineStart1;
public Transform LineEnd1;
public Transform LineStart2;
public Transform LineEnd2;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
/*
이 방법으로는 수직인 직선의 기울기가 0 또는 무한대가 되므로 교점을 찾을 수 없다.
*/
// 직선의 방정식 : y = ax + b, y = cx + d
// x` = (d - b) / (a - c)
// y` = ax` + b
float a = (LineEnd1.position.y - LineStart1.position.y) / (LineEnd1.position.x - LineStart1.position.x);
float c = (LineEnd2.position.y - LineStart2.position.y) / (LineEnd2.position.x - LineStart2.position.x);
float b = LineEnd1.position.y - a * LineEnd1.position.x;
float d = LineEnd2.position.y - c * LineEnd2.position.x;
if(a == c && b == d)
{
Debug.Log("Overlap");
return;
} else if (a == c)
{
Debug.Log("Parallel");
return;
} else
{
Debug.Log("Collision");
}
float x = (d - b) / (a - c);
float y = a * x + b;
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawLine(LineStart1.position, LineEnd1.position);
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(LineStart2.position, LineEnd2.position);
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(x, y, 0), 1);
Debug.Log(x + ", " + y);
}
}
선분의 충돌
직선의 교점이 두 선분의 영역안에 있는지 확인한다.
x축 방향 벡터가 0이면 기울기 계산 시 0으로 나누게 되므로 다른 처리가 필요하다.
- 기울기가 같다 : 평행
- 기울기가 같고 y절편이 다르다 : 평행
- 기울기가 같고 y절편이 같다 : 겹침
선분과 선분의 충돌
선분을 나타내는 방법
직선의 방정식으로 수직인 직선을 표현할 수 없으므로 매개변수 t를 사용하여 x와 y에 대한 방정식 2개로 선분을 표현한다.
\[\text{서로 다른 두 점 P1, P2로 이루어진 벡터 위의 한 점} \\ x = P1_x + (P2_x - P1_x)t \\ y = P1_y + (P2_y - P1_y)t\]직선의 매개변수 방정식
\[\begin{gather*} 직선의\ 매개변수\ 방정식\\ \begin{array}{ c c c } A( x_{1} ,\ y_{1}) & : & 직선을\ 지나는\ 점\\ \vec{u}( u_{1} ,u_{2}) & : & 직선의\ 방향\ 벡터\\ t & : & 실수 \end{array}\\ \\ \begin{matrix} ( x,\ y) & = & ( x_{1} ,\ y_{1}) \ +\ t( u_{1} ,\ u_{2})\\ & = & ( x_{1} +tu_{1} ,\ y_{1} +tu_{2}) \end{matrix}\\ \\ \therefore \begin{cases} x & = & x_{1} +tu_{1}\\ y & = & y_{1} +tu_{2} \end{cases} \Rightarrow 직선의\ t를\ 매개변수로\ 하는\ 매개변수\ 방정식 \end{gather*}\]선분과 선분의 충돌 이론
\[벡터 : P1 \to P2, Q1 \to Q2 \\ P(t) = P1 + (P2-P1)t \\ Q(s) = Q1 + (Q2-Q1)s \\ \text{교점이 있다는 것은 두 함수의 값이 같다는 것} \\ P(t) = Q(s) \\ \text{x 성분으로 전개} \\ P1_x + (P2_x - P1_x)t = Q1_x + (Q2_x - Q1_x)s \\ P1_x - Q1_x = (Q2_x - Q1_x)s - (P2_x - P1_x)t \\ \text{y 성분으로 전개} \\ P1_y + (P2_y - P1_y)t = Q1_y + (Q2_y - Q1_y)s \\ P1_y - Q1_y = (Q2_y - Q1_y)s - (P2_y - P1_y)t \\\] \[\text{위 식에서 t, s를 구하기 위해 행렬을 이용} \\ \begin{bmatrix} (Q2_x - Q1_x) & -(P2_x - P1_x) \\ (Q2_y - Q1_y) & -(P2_y - P1_y) \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} s \\ t \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} P1_x - Q1_x \\ P1_y - Q1_y \end{bmatrix} \\\\ \text{위 식을 } AX = B\text{ 형태로 봤을 때}\\ \text{좌변에 X만 남기기 위해서는 좌, 우변에 } A^{-1}\text{(역행렬)을 곱해야함} \\ X = BA^{-1} \\ \begin{matrix} \begin{bmatrix} s \\ t \end{bmatrix} &=& \frac{1} {\begin{vmatrix} (Q2_x - Q1_x) & -(P2_x - P1_x) \\ (Q2_y - Q1_y) & -(P2_y - P1_y) \end{vmatrix}} \begin{bmatrix} -(P2_y - P1_y) & -(P2_x - P1_x) * -1 \\ (Q2_y - Q1_y) * -1 & (Q2_x - Q1_x) \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} P1_x - Q1_x \\ P1_y - Q1_y \end{bmatrix} \\ &=& \frac{1} {\begin{vmatrix} (Q2_x - Q1_x) & (P1_x - P2_x) \\ (Q2_y - Q1_y) & (P1_y - P2_y) \end{vmatrix}} \begin{bmatrix} (P1_y - P2_y) & (P2_x - P1_x) \\ (Q1_y - Q2_y) & (Q2_x - Q1_x) \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} P1_x - Q1_x \\ P1_y - Q1_y \end{bmatrix} \\ &=& \frac{1}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \begin{bmatrix} (P1_y - P2_y) & (P2_x - P1_x) \\ (Q1_y - Q2_y) & (Q2_x - Q1_x) \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} P1_x - Q1_x \\ P1_y - Q1_y \end{bmatrix} \\ &=& \begin{bmatrix} \frac{(P1_y - P2_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} & \frac{(P2_x - P1_x)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \\ \frac{(Q1_y - Q2_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} & \frac{(Q2_x - Q1_x)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} P1_x - Q1_x \\ P1_y - Q1_y \end{bmatrix} \\ \end{matrix}\] \[\begin{matrix} \therefore t &=& \frac{(Q1_y - Q2_y)(P1_x - Q1_x)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} + \frac{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - Q1_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \\ &=& \frac{(Q1_y - Q2_y)(P1_x - Q1_x) + (Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - Q1_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \\ \therefore s &=& \frac{(P1_y - P2_y)(P1_x - Q1_x)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} + \frac{(P2_x - P1_x)(P1_y - Q1_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \\ &=& \frac{(P1_y - P2_y)(P1_x - Q1_x) + (P2_x - P1_x)(P1_y - Q1_y)}{(Q2_x - Q1_x)(P1_y - P2_y) - (P1_x - P2_x)(Q2_y - Q1_y)} \\ \end{matrix} \\\]선분과 선분의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_Segment_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform P1;
public Transform P2;
public Transform Q1;
public Transform Q2;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawLine(P1.position, P2.position);
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(Q1.position, Q2.position);
Vector3 p1 = P1.position;
Vector3 p2 = P2.position;
Vector3 q1 = Q1.position;
Vector3 q2 = Q2.position;
Vector3 v = P2.position - P1.position;
Vector3 w = Q2.position - Q1.position;
float denominator = (q2.x - q1.x) * (p1.y - p2.y) - (p1.x - p2.x) * (q2.y - q1.y);
if(denominator == 0)
{
Debug.Log("Overlap");
return;
}
// t : P1->P2에서 교점의 비율, s : Q1->Q2에서 교점의 비율
float t = ((q1.y - q2.y) * (p1.x - q1.x) + (q2.x - q1.x) * (p1.y - q1.y)) / denominator;
float s = ((p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.x - q1.x) + (p2.x - p1.x) * (p1.y - q1.y)) / denominator;
float x = v.x * t + p1.x;
float y = v.y * t + p1.y;
Debug.Log(t + ", " + s + ", " + denominator);
if (t < 0.0f || t > 1.0f || s < 0.0f || s > 1.0f)
{
Debug.Log("No Collision");
}
else if (t == 0 && s == 0)
{
Debug.Log("Parallel");
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(x, y, 0), 1);
}
}
}
선분과 구의 충돌
t를 사용하여 선분 위의 점 표현하기
\[x = P_x + V_xt \\ y = P_y + V_yt \\ z = P_z + V_zt \\\]t는 0.0 ~ 1.0 사이의 값
시작점 P
시작점에서의 벡터 V
선분위의 점 (x, y, z)
구의 방정식
\[\text{구의 방정식 표준형} \\ (a-x)^2+(b-y)^2+(c-z)^2=r^2\] \[\text{구의 방정식 일반형(표준형의 전개)} \\ x^2 + y^2 + z^2 - 2ax - 2by - 2cz + a^2 + b^2 + c^2 - r^2 = 0 \\ x^2 + y^2 + z^2 + Ax + By + Cz + D = 0\]중심 : (a, b, c) 반지름 : r 구면 위의 점 : (x, y, z)
이차 방정식의 근의 공식
\[ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \\ x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} }{2a}\]일차항에 상수 2가 곱해진 경우의 근의 공식
\[ax^2 + 2bx + c = 0 \\ x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-ac} }{a}\]근의 공식의 판별식(Discriminant)
\[D = b^2 - 4ac\]| D | 의미 |
|---|---|
| D > 0 | 서로 다른 두 근 |
| D = 0 | 중근(완전 제곱식, 근이 하나) |
| D < 0 | 근이 없다 |
선분과 구의 충돌 이론
\[\text{구의 방정식} : (x - S_x)^2 + (y - S_y)^2 + (z - S_z)^2 = r^2 \\ 선분 : x = V_xt + P_x, y = V_yt + P_y, z = V_zt + P_z \\ \text{구의 방정식에 선분의 요소를 대입} \\ (P_x + V_xt - S_x)^2 + (P_y + V_yt - S_y)^2 + (P_z + V_zt - S_z)^2 = r^2 \\ \text{다음과 같이 치환} \\ k_x = P_x - S_x \\ k_y = P_y - S_y \\ k_z = P_z - S_z \\ (k_x + V_xt)^2 + (k_y + V_yt)^2 + (k_z + V_zt)^2 = r^2 \\ \text{전개} \\ k_x^2 + 2k_xV_xt + V_x^2t^2 + k_y^2 + 2k_yV_yt + V_y^2t^2 + k_z^2 + 2k_zV_zt + V_z^2t^2 = r^2 \\ (V_x^2 + V_y^2 + V_z^2)t^2 + 2(k_xV_x + k_yV_y + k_zV_z)t + k_x^2 + k_y^2 + k_z^2 - r^2 \\ \text{다음과 같이 치환} \\ a = V_x^2 + V_y^2 + V_z^2 \\ b = k_xV_x + k_yV_y + k_zV_z \\ c = k_x^2 + k_y^2 + k_z^2 - r^2 \\ at^2 + 2bt + c = 0 \\ \text{근의 공식으로 t값을 구한다} \\ t = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-ac} }{a} \\ \therefore \text{t값을 구한 뒤 '선분 위의 점 방정식'에 대입하여 x, y, z 값을 구하면 된다.}\]S(x, y, z) : 구의 중심
r : 구의 반지름
t값의 의미
| t값의 개수 | t값의 범위 | 의미 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | 충돌 X |
| 1 | 0~1 사이 | 한 점에서 선분 충돌 O |
| 1 | 0~1 벗어남 | 선분 충돌 X, 직선 충돌 O |
| 2 | t값 하나만 0~1 사이 | 한 점에서 선분 충돌 O, 원에 걸침 |
| 2 | t값 둘 다 0~1 사이 | 두 점에서 선분 충돌 O, 원을 관통 t값이 작은 쪽이 시작점에 가깝다. |
실제 프로그램에서는 판별식으로 직선이 충돌했는지를 먼저 계산하면 불필요한 계산을 줄일 수 있다.
선분과 구의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_Sphere_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform P1;
public Transform P2;
public Transform Sphere;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 s = Sphere.position;
float r = Sphere.localScale.x * 0.5f;
Vector3 p = P1.position;
Vector3 v = P2.position - P1.position;
Vector3 k = new Vector3(p.x - s.x, p.y - s.y, p.z - s.z);
// ax^2 + 2bx + c = 0
float a = Mathf.Pow(v.x, 2) + Mathf.Pow(v.y, 2) + Mathf.Pow(v.z, 2);
float b = k.x * v.x + k.y * v.y + k.z * v.z;
float c = Mathf.Pow(k.x, 2) + Mathf.Pow(k.y, 2) + Mathf.Pow(k.z, 2) - Mathf.Pow(r, 2);
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(p, p + v);
// 판별식
float d = Mathf.Pow(b, 2) - (a * c);
if(d < 0) // 근이 없다
{
return;
}
// 근의 공식
float t1 = (-b + Mathf.Sqrt(d)) / a;
float t2 = (-b - Mathf.Sqrt(d)) / a;
Debug.Log(t1 + ", " + t2);
if (t1 >= 0f && t1 <= 1f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(v.x * t1 + p.x, v.y * t1 + p.y, v.z * t1 + p.z), 1);
}
if (t2 >= 0f && t2 <= 1f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(v.x * t2 + p.x, v.y * t2 + p.y, v.z * t2 + p.z), 1);
}
}
}
선분과 평면의 충돌
선분과 평면의 충돌 이론
\[\begin{matrix} l &:& \text{선분의 시작점과 평면의 최단 거리} \\ n &:& \text{평면 법선 벡터} \\ p &:& \text{평면 상의 한 점} \\ s &:& \text{선분의 시작점} \\ v &:& \text{선분의 벡터} \\ cos\theta &:& \text{평면 법선 벡터와 선분 벡터의 내적값} \\ w &:& \text{선분의 시작점과 선분과 평면이 충돌하는 지점까지의 벡터} \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} l\text{을 구하기 위해 s를 평면 방정식에 대입한다.} \\ l = n_x(s_x - p_x) + n_y(s_y - p_y) + n_z(s_z - p_z) \\ \text{평면 법선 벡터와 선분 벡터의 방향을 맞추고 내적으로 cos값을 구한다.} \\ \cos\theta = \hat{v} \cdot -\hat{n} \\ w\text{를 구한다.} \\ w = \frac{l}{\cos\theta} \times \hat{v} \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} 비교 & 충돌 여부 \\ \rVert w \lVert < 0 & X \\ \rVert w \lVert < \rVert v \lVert & O \\ \rVert w \lVert > \rVert v \lVert & X \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\\]선분과 평면의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_Plane_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform Plane;
public Transform SegmentStart;
public Transform SegmentEnd;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
/*
법선 벡터 : N(Nx, Ny, Nz)
평면상의 한 점 : P(Px, Py, Pz)
평면의 방정식 : Nx*x + Ny*y + Nz*z + d = 0
d = -N·Q = -(Nx*Px + Ny*Py + Nz*Pz)
*/
Vector3 n = Plane.up.normalized; // 평면의 법선 벡터
Vector3 p = Plane.position; // 평면상의 한 점
Vector3 s = SegmentStart.position; // 선분의 시작점
// d값은 변하지 않기 때문에 미리 계산하는게 좋다.
float d = -(n.x * p.x + n.y * p.y + n.z * p.z);
// 선분의 시작점과 평면의 거리
float distance = n.x * s.x + n.y * s.y + n.z * s.z + d; // 평면의 방정식의 근
// 평면의 방정식의 근이 0보다 작을 경우 공간상의 점은 평면 법선 벡터가 있는 쪽의 반대쪽에 있다.
if(distance < 0)
{
n *= -1; // 선분의 시작점이 법선 벡터 반대쪽에 있으므로 법선 벡터를 뒤집어 준다.
distance *= -1; // 거리에서 방향 정보를 제거한다.
}
// 공간 상의 점과 평면을 연결하는 가장 짧은 벡터
Vector3 shortestVector = n * distance;
// 선분 벡터
Vector3 segment = SegmentEnd.position - SegmentStart.position;
// 평면의 법선 벡터와 선분의 각도
float cos = Vector3.Dot(-n, segment.normalized);
// 선분과 평면의 각도가 0~90 사이일 경우만 계산한다.
// 90~180 사이에서는 선분의 방향으로 절대 만나지 않는다.
if (cos > 0)
{
// 선분의 시작에서 평면까지의 거리
float distanceFromStartToPlane = distance / cos;
// 선분의 시작에서 평면까지의 벡터
Vector3 toPlane = segment.normalized * distanceFromStartToPlane;
Debug.Log(distanceFromStartToPlane + ", " + segment.magnitude);
// 제곱근 연산은 부하가 크기 때문에 길이의 제곱으로 비교한다.
//if (distanceFromStartToPlane <= segment.magnitude)
if (Mathf.Pow(distanceFromStartToPlane, 2) <= segment.sqrMagnitude)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(SegmentStart.position + toPlane, 1);
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan; // 선분과 평면이 충돌함
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 선분과 평면이 충돌하지 않음
}
} else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 선분과 평면이 충돌하지 않음
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(SegmentStart.position, SegmentEnd.position);
}
}
선분과 삼각형의 충돌
선분과 삼각형의 충돌 이론
\[\begin{matrix} ip &:& \text{선분과 삼각형의 면이 만나는 점(intersection point)} \\ t1, t2, t3 &:& \text{삼각형의 꼭지점(triangle)} \\ n1, n2, n3 &:& \text{p와 t1, t2, t3을 잇는 벡터와 각 변을 외적한 법선 벡터(normal)} \\ c1, c2 &:& \text{v1, v2, v3를 내적한 값(cos)} \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} ip\text{와 t1, t2, t3을 잇는 벡터와 각 변을 외적하여 법선 벡터를 구한다.} \\ n1 = (t1 - ip) \times (t3 - t1) \\ n2 = (t2 - ip) \times (t1 - t2) \\ n3 = (t3 - ip) \times (t2 - t3) \\ \text{법선 벡터들을 내적한다.} \\ c1 = n1 \cdot n2 \\ c2 = n2 \cdot n3 \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \therefore c1 > 1 ~\And~ c2 > 1 \rightarrow \text{충돌점이 삼각형 내부에 있다.} \\ (\because \text{내적의 결과 1이면 0도, -1이면 180도이다.})\]선분과 삼각형의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_Triangle_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform T1;
public Transform T2;
public Transform T3;
public Transform SP1;
public Transform SP2;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
/*
법선 벡터 : N(Nx, Ny, Nz)
평면상의 한 점 : P(Px, Py, Pz)
평면의 방정식 : Nx*x + Ny*y + Nz*z + d = 0
d = -N·Q = -(Nx*Px + Ny*Py + Nz*Pz)
*/
// 삼각형 선분 벡터
Vector3 tv12 = T2.position - T1.position;
Vector3 tv23 = T3.position - T2.position;
Vector3 tv31 = T1.position - T3.position;
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, T2.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, T3.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, T1.position);
Vector3 tn = Vector3.Cross(tv12, tv23); // 삼각형의 법선 벡터(triangle normal)
Vector3 tp = T1.position; // 삼각형 위의 한 점(triangle point)
Vector3 sp = SP1.position; // 선분의 시작점(start or segment point)
// d값은 변하지 않기 때문에 미리 계산하는게 좋다.
float d = -(tn.x * tp.x + tn.y * tp.y + tn.z * tp.z);
// 선분의 시작점과 평면의 거리
float distance = tn.x * sp.x + tn.y * sp.y + tn.z * sp.z + d; // 평면의 방정식의 근(평면과 점의 거리)
// 평면의 방정식의 근이 0보다 작을 경우 공간상의 점은 평면 법선 벡터가 있는 쪽의 반대쪽에 있다.
if (distance < 0)
{
tn *= -1; // 선분의 시작점이 법선 벡터 반대쪽에 있으므로 법선 벡터를 뒤집어 준다.
distance *= -1; // 거리에서 방향 정보를 제거한다.
}
// 공간 상의 점과 평면을 연결하는 가장 짧은 벡터
Vector3 shortestVector = tn * distance;
// 선분 벡터(segment vector)
Vector3 sv = SP2.position - SP1.position;
// 평면의 법선 벡터와 선분의 각도
float cos = Vector3.Dot(-tn, sv.normalized);
// 선분과 평면의 각도가 0~90 사이일 경우만 계산한다.
// 90~180 사이에서는 선분의 방향으로 절대 만나지 않는다.
if (cos > 0)
{
// 선분의 시작에서 평면까지의 거리
float distanceFromStartToPlane = distance / cos;
// 선분의 시작에서 평면까지의 벡터(intersection point vector)
Vector3 ipv = sv.normalized * distanceFromStartToPlane;
// 제곱근 연산은 부하가 크기 때문에 길이의 제곱으로 비교한다.
if (Mathf.Pow(distanceFromStartToPlane, 2) <= sv.sqrMagnitude)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(SP1.position + ipv, 1);
// 각 변과 충돌 지점에서 각 꼭지점으로 이은 선을 외적하여 나온 벡터들을
// 서로 내적하여 모두 같은 값이면 삼각형 안에 있다고 판단
Vector3 ip = SP1.position + ipv; // 충돌 지점(intersection point)
Vector3 n1 = Vector3.Cross(tv31, T1.position - ip).normalized;
Vector3 n2 = Vector3.Cross(tv12, T2.position - ip).normalized;
Vector3 n3 = Vector3.Cross(tv23, T3.position - ip).normalized;
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, T1.position + n1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, T2.position + n2);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, T3.position + n3);
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, ip);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, ip);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, ip);
// 내적이 1이면 같은 방향
Debug.Log(Vector3.Dot(n1, n2) + ", " + Vector3.Dot(n2, n3));
if (Vector3.Dot(n1, n2) == 1f && Vector3.Dot(n2, n3) == 1f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan; // 선분과 삼각형이 충돌함
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 선분과 삼각형이 충돌하지 않음
}
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 선분과 삼각형이 충돌하지 않음
}
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 선분과 삼각형이 충돌하지 않음
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(SP1.position, SP2.position);
}
}
구와 구의 충돌
구와 구의 충돌 이론
\[\begin{matrix} sp1, sp2 &:& \text{구의 중심점(sphere point)} \\ v &:& \text{두 구의 중심점을 잇는 벡터(vector)} \\ r1, r2 &:& \text{구의 반지름(radius)} \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} v = sp2 - sp1 \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} \therefore \rVert v \lVert < r1 + r2 \Rightarrow 충돌 \\ \\ \text{컴퓨터에서 제곱근 연산을 피하려면 제곱하여 비교한다.} \\ v_x^2 + v_y^2 + v_z^2 < (r1 + r2)^2 \Rightarrow 충돌 \\ \\ \end{matrix}\\ \text{충돌한 만큼 밀어내기} \\ \begin{matrix} idst &:& \text{침범한 거리(invasion distance)} \\ nsp &:& \text{밀려난 새로운 위치(new sphere point)} \\ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix} idst = (r1 + r2) - \rVert v \lVert \\ \therefore nsp = -\hat{v} \times idst \\ \\ \end{matrix}\]구와 구의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Sphere_Sphere_Collision : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform S1;
public Transform S2;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 sp1 = S1.position;
Vector3 sp2 = S2.position;
float r1 = S1.localScale.x * 0.5f;
float r2 = S2.localScale.x * 0.5f;
Vector3 v = sp2 - sp1;
if (v.sqrMagnitude < Mathf.Pow(r1 + r2, 2))
{
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
// 침범한 만큼 밀어내기
// 침범한 거리(invasion distance)
float idst = (r1 + r2) - v.magnitude;
S1.position += -v.normalized * idst;
} else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(sp1, sp2);
}
}
구와 삼각형의 충돌
구와 삼각형의 충돌 이론
- 구와 평면의 충돌 검사
- 삼각형 각 변과 구의 충돌 검사 - 구와 선분의 충돌 이용
- 구가 삼각형 안에 있는지 검사 - 선분과 삼각형 충돌 이용
구와 삼각형의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Sphere_Triangle_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform T1;
public Transform T2;
public Transform T3;
public Transform SP;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// 삼각형 선분 벡터(triangle vector)
Vector3 tv12 = T2.position - T1.position;
Vector3 tv23 = T3.position - T2.position;
Vector3 tv31 = T1.position - T3.position;
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, T2.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, T3.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, T1.position);
Vector3 tn = Vector3.Cross(tv12, tv23).normalized; // 삼각형의 법선 벡터(triangle normal)
Vector3 pp = T1.position; // 평면 위의 한 점(plane point)
Vector3 sp = SP.position; // 구의 중심(sphere point)
float r = SP.localScale.x * 0.5f; // 구의 반지름(radius)
// d값은 변하지 않기 때문에 미리 계산하는게 좋다.
float d = -(tn.x * pp.x + tn.y * pp.y + tn.z * pp.z); // 평면의 방정식에서 d값
// 구의 중심과 평면의 거리
float distance = tn.x * sp.x + tn.y * sp.y + tn.z * sp.z + d; // 평면의 방정식의 근(평면과 점의 거리)
// 평면의 방정식의 근이 0보다 작을 경우 공간상의 점은 평면 법선 벡터가 있는 쪽의 반대쪽에 있다.
if (distance < 0)
{
tn *= -1; // 선분의 시작점이 법선 벡터 반대쪽에 있으므로 법선 벡터를 뒤집어 준다.
distance *= -1; // 거리에서 방향 정보를 제거한다.
}
// 1. 구와 삼각형이 있는 평면과 충돌 검사 //
{
if (distance > r)
{
return;
}
}
// 2. 구와 삼각형 각 변의 충돌 검사 //
{
bool isCollided = false;
Vector3[] tps = { T1.position, T2.position, T3.position };
Vector3[] tvs = { tv12, tv23, tv31 };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Vector3 tp = tps[i];
Vector3 tv = tvs[i];
Vector3 k = new Vector3(tp.x - sp.x, tp.y - sp.y, tp.z - sp.z);
// ax^2 + 2bx + c = 0
float a = Mathf.Pow(tv.x, 2) + Mathf.Pow(tv.y, 2) + Mathf.Pow(tv.z, 2);
float b = k.x * tv.x + k.y * tv.y + k.z * tv.z;
float c = Mathf.Pow(k.x, 2) + Mathf.Pow(k.y, 2) + Mathf.Pow(k.z, 2) - Mathf.Pow(r, 2);
// 판별식(discriminant)
float dis = Mathf.Pow(b, 2) - (a * c);
if (dis >= 0) // 근이 있다.
{
isCollided = true;
// 근의 공식
float t1 = (-b + Mathf.Sqrt(dis)) / a;
float t2 = (-b - Mathf.Sqrt(dis)) / a;
Debug.Log(t1 + ", " + t2);
if (t1 >= 0f && t1 <= 1f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(tv.x * t1 + tp.x, tv.y * t1 + tp.y, tv.z * t1 + tp.z), 0.2f);
}
if (t2 >= 0f && t2 <= 1f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(new Vector3(tv.x * t2 + tp.x, tv.y * t2 + tp.y, tv.z * t2 + tp.z), 0.2f);
}
}
if (isCollided) break;
}
if (isCollided)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(sp, r * 1.2f);
return;
}
}
// 3. 구가 삼각형 안에 들어갔는지 검사 //
{
// 구의 중심에서 삼각형에 수직으로 내린 직선 벡터(vertical vector)
Vector3 vv = tn * distance;
Vector3 ip = SP.position - vv; // 충돌 지점(intersection point)
Vector3 n1 = Vector3.Cross(tv31, T1.position - ip).normalized;
Vector3 n2 = Vector3.Cross(tv12, T2.position - ip).normalized;
Vector3 n3 = Vector3.Cross(tv23, T3.position - ip).normalized;
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, T1.position + n1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, T2.position + n2);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, T3.position + n3);
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, ip);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, ip);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T3.position, ip);
// 내적이 1이면 같은 방향
Debug.Log(Vector3.Dot(n1, n2) + ", " + Vector3.Dot(n2, n3));
if (Vector3.Dot(n1, n2) >= 0.0f && Vector3.Dot(n2, n3) >= 0.0f)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan; // 구가 삼각형 안에 있음
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red; // 구가 삼각형 안에 없음
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(SP.position, SP.position + vv);
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(SP.position, r*1.2f);
}
}
}
평면과 평면의 충돌
평면과 평면의 충돌 이론
두 평면의 교선
두 평면은 충돌시 하나의 직선에서 만나며 이 직선은 두 평면의 법선 벡터의 외적으로 구할 수 있다.
\[\begin{gather*} \begin{array}{ c c c } n_{0}( a_{0} ,\ b_{0} ,\ c_{0}) & : & 평면의\ 법선\ 벡터\\ n_{1}( a_{1} ,\ b_{1} ,\ c_{1}) & : & 평면의\ 법선\ 벡터\\ V & : & 두\ 평면의\ 교선 \end{array}\\ \\ \begin{array}{ c c l } V & = & n_{0} \ \times n_{1}\\ & = & ( b_{0} c_{1} -c_{0} b_{1} ,\ c_{0} a_{1} -a_{0} c_{1} ,\ a_{0} b_{1} -b_{0} a_{1})\\ & = & ( V_{x} ,\ V_{y} ,\ V_{z}) \end{array} \end{gather*}\]두 평면의 교선의 시작점
시작점은 교선위의 점의 요소중 하나를 0으로 만들어 찾아낸다.
이 때 법선 벡터의 요소중 0으로 만든 요소와 같은 요소가 0이라면 x, y 값을 계산할 수 없기 때문에 다른 요소를 0으로 만들어 찾아봐야한다.
\[\begin{gather*} \begin{array}{ c c l } a_{0} x\ +\ b_{0} y\ +\ c_{0} z\ +\ d_{0} \ =\ 0 & : & \text{평면 방정식 1}\\ a_{1} x\ +\ b_{1} y\ +\ c_{1} z\ +\ d_{1} \ =\ 0 & : & \text{평면 방정식 2} \end{array} \ \\ \\ z\ =\ 0\text{으로 고정한 후 평면 방정식}\\ a_{0} x\ +\ b_{0} y\ +\ d_{0} \ =\ 0\ \cdots ( 1)\\ a_{1} x\ +\ b_{1} y\ +\ d_{1} \ =\ 0\cdots ( 2)\\ \\ \text{(1)을 y에 대해 정리한다.}\\ \ b_{0} y\ =\ -( a_{0} x\ +\ d_{0})\\ y\ =\ \frac{-( a_{0} x\ +\ d_{0})}{b_{0}}\\ \\ (1)을\ (2)에\ 대입하고\ x에\ 대해\ 정리\\ \begin{array}{ r c c } a_{1} x\ +\ b_{1}\left(\frac{-( a_{0} x\ +\ d_{0})}{b_{0}}\right) \ +\ d_{1} & = & 0\\ a_{1} x-\frac{a_{0} b_{1} x}{b_{0}} -\frac{b_{1} d_{0}}{b_{0}} +d_{1} & = & 0\\ \frac{a_{1} b_{0}}{b_{0}} x-\frac{a_{0} b_{1}}{b_{0}} x-\frac{b_{1} d_{0}}{b_{0}} +d_{1} & = & 0\\ \frac{( a_{1} b_{0} -a_{0} b_{1})}{b_{0}} x-\frac{b_{1} d_{0}}{b_{0}} +d_{1} & = & 0\\ \cancel{b_{0}}\frac{( a_{1} b_{0} -a_{0} b_{1})}{\cancel{b_{0}}} x-\cancel{b_{0}}\frac{b_{1} d_{0}}{\cancel{b_{0}}} +b_{0} d_{1} & = & 0\\ ( a_{1} b_{0} -a_{0} b_{1}) x\ -b_{1} d_{0} \ +b_{0} d_{1} & = & 0\\ ( a_{1} b_{0} -a_{0} b_{1}) x & = & -( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})\\ x & = & \frac{-( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{( a_{1} b_{0} -a_{0} b_{1})}\\ x & = & \frac{-( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{-( a_{0} b_{1} -a_{1} b_{0})}\\ x & = & \frac{( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{( a_{0} b_{1} -a_{1} b_{0})}\\ \therefore x & = & \frac{( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{V_{z}} \end{array}\\ \\ 같은\ 방식으로\ y도\ 구할\ 수\ 있다.\\ \begin{array}{ c c c } \therefore x & = & \frac{( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{V_{z}}\\ \therefore y & = & \frac{( a_{1} d_{0} -a_{0} d_{1})}{V_{z}}\\ \therefore z & = & 0 \end{array}\\ \\ 이\ 때\ V_{z} 가\ 0이라면\ x,\ y값을\ 구할\ 수\ 없기\ 때문에\ \ \\ 다른\ 요소를\ 0으로\ 두고\ 위의\ 방식으로\ 찾는다.\\ \\ 아래는\ 시작점을\ 찾을\ 수\ 있는\ 조건표이다.\\ \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline x & y & z & 조건\\ \hline \frac{( b_{0} d_{1} -b_{1} d_{0})}{V_{z}} & \frac{( a_{1} d_{0} -a_{0} d_{1})}{V_{z}} & 0 & V_{z} \ \neq 0\\ \hline \frac{( c_{1} d_{0} -c_{0} d_{1})}{V_{y}} & 0 & \frac{( a_{0} d_{1} -a_{1} d_{0})}{V_{y}} & V_{y} \ \neq 0\\ \hline 0 & \frac{( c_{0} d_{1} -c_{1} d_{0})}{V_{x}} & \frac{( b_{1} d_{0} -b_{0} d_{1})}{V_{x}} & V_{x} \ \neq 0\\ \hline \end{array}\\ \\ V_{z} 가\ 0인\ 경우\ :\ 법선\ 벡터가\ z축에\ 직교함으로\ 인해\ 평면이\ z축에\ 평행한\ 경우\\ V_{y} 가\ 0인\ 경우\ :\ 법선\ 벡터가\ y축에\ 직교함으로\ 인해\ 평면이\ y축에\ 평행한\ 경우\\ V_{x} 가\ 0인\ 경우\ :\ 법선\ 벡터가\ x축에\ 직교함으로\ 인해\ 평면이\ x축에\ 평행한\ 경우\\ \\ 만약\ V_{x} ,\ V_{y} ,\ V_{x} 가\ 모두\ 0이라면\ 두\ 평면은\ 평행하기\ 때문에\ 교선이\ 없다.\\ \\ \end{gather*}\]평면과 평면의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Plane_Plane_Collision : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform P0;
public Transform P1;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 p0 = P0.position;
Vector3 p1 = P1.position;
// 평면의 법선
Vector3 n0 = P0.up.normalized;
Vector3 n1 = P1.up.normalized;
// 평면의 방정식의 d값
float d0 = -1 * Vector3.Dot(n0, p0);
float d1 = -1 * Vector3.Dot(n1, p1);
// 교선 벡터
Vector3 v = Vector3.Cross(P0.up, P1.up);
Debug.Log(v);
// 시작점
float x = 0;
float y = 0;
float z = 0;
if (v.z != 0.0f)
{
x = (n0.y * d1 - n1.y * d0) / v.z;
y = (n1.x * d0 - n0.x * d1) / v.z;
z = 0f;
}
else if (v.y != 0.0f)
{
x = (n1.z * d0 - n0.z * d1) / v.y;
y = 0f;
z = (n1.y * d0 - n0.y * d1) / v.z;
}
else if (v.x != 0.0f)
{
x = 0f;
y = (n0.z * d1 - n1.z * d0) / v.x;
z = (n1.y * d0 - n0.y * d1) / v.x;
}
Vector3 sp = new Vector3(x, y, z);
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawLine(p0, p0 + P0.up);
Gizmos.DrawLine(p1, p1 + P1.up);
Gizmos.color = Color.magenta;
Gizmos.DrawWireMesh(P0.gameObject.GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh, P0.position, P0.rotation, P0.localScale);
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, v*100000f);
Gizmos.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, -v*100000f);
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawLine(sp, sp + v * 100000f);
Gizmos.DrawLine(sp, sp + -v * 100000f);
}
}
평면과 삼각형의 충돌
평면과 삼각형의 충돌 이론
- 삼각형의 꼭지점들이 평면의 다른 쪽에 위치했는지 확인한다.
- 평면의 방정식에 꼭지점을 대입하여 나온 거리값이 양수이면 평면의 법선쪽, 음수이면 법선 반대쪽이다.
- 삼각형의 변과 평면의 교점은 ‘평면과 선분의 충돌’을 이용한다.
- 삼각현의 변의 벡터 방향이 평면을 향하지 않고 있다면 충돌하지 않으므로 무시한다.
평면과 삼각형의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Plane_Triangle_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform T0;
public Transform T1;
public Transform T2;
public Transform P; // Plane
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 p = P.position;
Vector3 t0 = T0.position;
Vector3 t1 = T1.position;
Vector3 t2 = T2.position;
// 평면의 법선
Vector3 n = P.up;
// 평면의 방정식의 d값
float d = -1 * Vector3.Dot(n, p);
float distance0 = n.x * t0.x + n.y * t0.y + n.z * t0.z + d;
float distance1 = n.x * t1.x + n.y * t1.y + n.z * t1.z + d;
float distance2 = n.x * t2.x + n.y * t2.y + n.z * t2.z + d;
Debug.Log(distance0 + ", " + distance1 + ", " + distance2);
Color color = Color.white;
// 모두 같은 부호이면 같은 면에 있다. - 충돌 안함
// 하나라도 부호가 다르면 다른 면에 있다. - 충돌함.
if (distance0 * distance1 <= 0 || distance1 * distance2 <= 0)
{
// 충돌한 지점 찾기
Vector3[] ts = { t0, t1, t2 }; // 꼭지점 위치
Vector3[] tvs = { t1 - t0, t2 - t1, t0 - t2 }; // 변
float[] distances = { distance0, distance1, distance2 }; // 꼭지점과 평면의 거리
for (int i = 0; i < tvs.Length; i++)
{
Vector3 tv = tvs[i];
Vector3 tvn = tv.normalized;
float distance = distances[i];
if (distance > 0 && Vector3.Dot(n, tvn) > 0) continue; // 변이 평면 위에 있고 평면을 향하고 있지 않다.
if (distance < 0 && Vector3.Dot(n, tvn) < 0) continue; // 변이 평면 아래에 있고 평면을 향하고 있지 않다.
distance = Mathf.Abs(distance); // 평면 위, 아래 판단 후 절대값으로 만들어 방향 정보를 제거한다.
float cos = Mathf.Abs(Vector3.Dot(tvn, n)); // cos의 절대값은 예각이다.
float l = distance / cos; // 꼭지점에서 변의 방향으로 평면에 닿을 때까지의 거리
if (l >= 0f && Mathf.Pow(l, 2) <= tv.sqrMagnitude) // 이 변이 평면과 충돌
{
Vector3 v = tvn * l; // 꼭지점에서 평면에 닿을 때까지의 벡터
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(ts[i] + v, 0.5f);
}
}
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(T0.position, T1.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T1.position, T2.position);
Gizmos.DrawLine(T2.position, T0.position);
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(P.position, P.position + P.up * 5f);
}
}
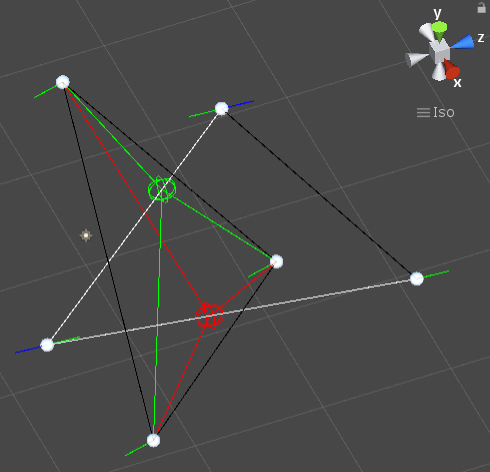
삼각형과 삼각형의 충돌
삼각형과 삼각형의 충돌 이론
- 한 변이 다른 삼각형 안에 있는 경우
- 두 삼각형 중 하나의 삼각형의 모든 변을 조사한다.
- 두 변이 다른 삼각형 안에 있는 경우
- 하나의 삼각형의 두 변 모두 다른 삼각형 안에 있는지 각각 조사한다.
한 변이 다른 삼각형을 통화하는지 6개의 변에 대해 검사하면 두 변이 다른 삼각형에 포함됐는지를 검사안해도 된다.
코드는 이 방식으로 구현했다.
삼각형과 삼각형의 충돌 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// 삼각형 클래스 정의 --- 시작
[System.Serializable]
public class Triangle
{
public Transform[] Vertices; // 꼭짓점
public Vector3[] Segments; // 선분
public Vector3 N; // 법선 벡터
public Color[] SegmentColors = new Color[3]; // 각 선분의 색상, 충돌한 선분은 다른 색으로 칠해준다.
private float _d; // 평면의 방정식의 d
// 삼각형을 초기화한다
public void Init()
{
if (Segments == null || Segments.Length < Vertices.Length) Segments = new Vector3[Vertices.Length];
Segments[0] = Vertices[1].position - Vertices[0].position; // 0->1로 향하는 벡터
Segments[1] = Vertices[2].position - Vertices[1].position; // 1->2로 향하는 벡터
Segments[2] = Vertices[0].position - Vertices[2].position; // 2->0로 향하는 벡터
N = Vector3.Cross(Segments[0], Segments[1]).normalized; // 평면의 법선(노멀) 벡터는 자주사용하므로 미리 계산
_d = -(Vector3.Dot(N, Vertices[0].position)); // 평면의 방정식의 d값은 자주 사용하므로 미리 계산
for (int i = 0; i < SegmentColors.Length; i++)
{
SegmentColors[i] = Color.black; // 충돌하지 않은 선분 기본 색상 초기화
}
}
// 현재 삼각형을 평면으로 하여 매개변수로 전달된 선분과 충돌했는지 테스트한다.
// 선분에서 충돌한 지점을 선분 길이 대비 비율로 반환한다.(직선의 매개변수 방정식에서 t)
// 0~1 사이 : 충돌 지점이 선분 안이다. 충돌했다.
// 0~1 바깥 : 충돌 지점이 선분 밖이다. 충돌 안했다.
public float HitTestWithSegment(Vector3 position, Vector3 vector)
{
// 평면과 선분 시작점의 거리
float distance = N.x * position.x + N.y * position.y + N.z * position.z + _d;
// 선분의 방향을 나타내는 단위벡터
Vector3 vn = vector.normalized;
// 반환할 충돌지점 비율값(직선의 매개변수 방정식에서 t)
float t = -1f;
// 평면의 법선과 선분의 내적값, 두 벡터 사이각의 cos값과 같다.
float cos = Vector3.Dot(N, vn);
// 평면과 시작점의 거리가 양수이면 시작점은 평면의 법선벡터 방향(평면의 위)에 있고,
// 음수이면 평면의 법선벡터 반대 방향(평면 아래)에 있다.
if (distance > 0 && cos > 0) return t; // 평면 위에 있고 평면을 향하지 않는다. 충돌 가능성 없음.
if (distance < 0 && cos < 0) return t; // 평면 아래에 있고 평면을 향하지 않는다. 충돌 가능성 없음.
distance = Mathf.Abs(distance); // 거리에서 방향성을 제거하기 위해 부호를 제거한다.
cos = Mathf.Abs(cos); // 예각을 구하기 위해 절대값으로 변경(cos값에서 부호를 제거하면 언제나 0~90사이를 가리키는 예각이 된다.)
// 두 벡터의 내각, 즉 cos값이 0이라는 것은 두 벡터가 90도로 직교한다는 것이고 이는
// 평면의 법선과 선분이 90도라는 것이다.
// 즉, 평면과 선분은 평행하므로 충돌 가능성이 없다.
if (Mathf.Approximately(cos, 0f)) return t;
// 시작점에서 평면에 내린 수선(평면에 직교하는 선 = 인접변)의 길이와
// 두 벡터의 cos값으로 빗변의 길이를 알아낸다.
float hypotenuse = distance / cos;
// 빗변의 길이와 선분의 길이의 비율을 계산한다.
t = hypotenuse / vector.magnitude;
return t;
}
// 선분을 모두 그린다.
public void DrawSegments()
{
for (int i = 0; i < Segments.Length; i++)
{
Gizmos.color = SegmentColors[i];
Gizmos.DrawLine(Vertices[i].position, Vertices[(i + 1) % Segments.Length].position);
}
}
}
/// 삼각형 클래스 정의 --- 끝
public class Triangle_Triangle_Collision : MonoBehaviour {
public Triangle t0; // 삼각형1
public Triangle t1; // 삼각형2
private Color[] _crossVectorColors = { Color.red, Color.blue, Color.green };
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// 삼각형을 초기화한다.
t0.Init();
t1.Init();
// t0을 평면으로 하여 충돌 테스트를 한다.
bool hit = HitTestTriangle(t0, t1);
// 충돌하지 않았으면 t1을 평면으로 하여 충돌 테스트를 한 번 더 한다.
if (!hit) HitTestTriangle(t1, t0);
// 삼각형의 외곽선을 그린다.
t0.DrawSegments();
t1.DrawSegments();
}
// 삼각형을 평면과 선분 역할로 구분하여 충돌 테스트를 한다.
private bool HitTestTriangle(Triangle triangleForPlane, Triangle triangle)
{
bool hit = false;
// 각각의 선분이 삼각형과 걸치는지 확인
for (int i = 0; i < triangle.Segments.Length; i++)
{
Color segmentColor = Color.black;
// 현재 선분과 삼각형의 평면이 충돌하는지 확인, 선분 길이 대비 충돌지점의 비율을 반환 받는다.
float t = triangleForPlane.HitTestWithSegment(triangle.Vertices[i].position, triangle.Segments[i]);
if (t >= 0f && t <= 1f) // 삼각형의 평면과 선분이 충돌했다.
{
// 삼각형의 평면과 선분의 히트 포인트(충돌 지점)
Vector3 hitPoint = triangle.Vertices[i].position + triangle.Segments[i] * t;
// 히트 포인트가 삼각형 안에 있는지 확인
Vector3[] crossVectors = new Vector3[triangleForPlane.Segments.Length];
for (int jj = 0; jj < triangleForPlane.Segments.Length; jj++)
{
// 각 꼭지점에서 히트 포인트까지 벡터를 구하고 인접변과 외적한다.
Vector3 toHitPoint = hitPoint - (triangleForPlane.Vertices[jj].position + triangleForPlane.Segments[jj]);
crossVectors[jj] = Vector3.Cross(triangleForPlane.Segments[jj], toHitPoint);
// 외적 벡터 그리기
Gizmos.color = _crossVectorColors[i];
Gizmos.DrawLine(triangleForPlane.Vertices[jj].position, triangleForPlane.Vertices[jj].position + crossVectors[jj].normalized * 3f);
}
// 외적한 모든 벡터가 같은 방향이면 히트 포인트는 삼각형 안에 있다.
// 같은 방향의 벡터끼리 내적하면 1~0(0~90도) 양수, 다른 방향의 벡터끼리 내적하면 0~-1(90~180도) 음수
if (Vector3.Dot(crossVectors[0], crossVectors[1]) > 0 && Vector3.Dot(crossVectors[1], crossVectors[2]) > 0)
{
hit = true;
segmentColor = Color.white; // 충돌했으므로 선분색을 변경한다.
Gizmos.color = _crossVectorColors[i]; // 충돌지점마다 색을 다르게 한다.
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(hitPoint, 1f); // 충돌지점을 그린다.
for (int jj = 0; jj < triangleForPlane.Segments.Length; jj++)
{
Gizmos.DrawLine(triangleForPlane.Vertices[jj].position, hitPoint); // 꼭짓점과 충돌지점까지 선을 그린다.
}
}
}
triangle.SegmentColors[i] = segmentColor;
}
return hit;
}
}