[TOC]
충돌 판정의 고속화
평면의 앞뒤 확인
충돌을 앞으로만 한정하여 평면의 충돌 테스트 대상을 줄일 수 있다.
충돌 대상의 각 면의 법선 벡터와 충돌 방향을 내적하여 서로 마주보고 있다면(각도가 90~180 사이) 충돌 테스트 대상으로 선정한다.
충돌 영역의 간략화
실제 게임에서 충돌 영역이 미세하지 않아도 게임 플레이에 지정을 주지 않는 경우가 많다.
이럴 때 충돌 영역을 구와 같이 간단한 형태로 만들어 충돌 검출에 필요한 계산을 줄일 수 있다.
영역 분할
충돌 오브젝트가 있는 영역을 분할하여 충돌 대상이 속한 영역의 오브젝트만 충돌 검출한다.
바운딩 볼륨
실제 충돌 테스트할 대상을 충돌체로 감싸고 이 충돌체가 충돌했을 때 실제 대상과 충돌 테스트를 하는 방법으로 실제 충돌 대상의 복잡한 충돌 테스트를 필요할 때만 할 수 있다.
감싸는 충돌체는 충돌 판정을 쉽게 할 수 있는 구, 박스 형태가 사용된다.
바운딩 스피어
구 형태의 바운딩 볼륨이다.
구는 선분과 충돌 판정이 복잡하므로 구끼리 충돌 판정하는 것이 좋다.
충돌 판정이 쉽고 구조가 간단해서 메모리를 적게 사용하는 장점이 있지만 실제 객체를 감쌀 때 빈 공간이 생기기 쉽다.
바운딩 박스
박스 형태의 바운딩 볼륨이다.
구보다 빈틈없이 객체를 감쌀 수 있다.
바운딩 볼륨 검출 방법
AABB(Axis-Aligned Bounding Box)
AABB 이론
x, y, z축에 평행한 변을 갖는 상자로 객체가 회전해도 상자는 회전하지 않는다.
두 점으로 상자를 만들고 선분과 충돌하는 영역을 계산한다.
선분과 충돌하는 영역은 x, y, z축으로 나누어 계산하고 이 영역들이 모두 겹치는 영역이 있을 경우 충돌로 판정한다.
- 박스의 x축과 선분의 충돌 영역 tx_min, tx_max를 구하고 이 값이 0~1 사이에 있다면 이 값으로 t_min, t_max 값을 갱신한다.
- y, x축에 대해서도 같은 과정을 거친다.
- 최종적으로 모든 축과 겹치는 t_min, t_max 값이 나온다.
- 이 값으로 다음 조건에 따라 충돌 판정을 내린다.
AABB 구현
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_AABB_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform B0; // Box0
public Transform B1; // Box1
public Transform S0; // Segment0
public Transform S1; // Segment1
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 b0 = B0.position;
Vector3 b1 = B1.position;
Vector3 s0 = S0.position;
Vector3 s1 = S1.position;
Vector3 sv = s1 - s0;
// 선분과 박스의 충돌하는 곳의 최대, 최소값.(직선의 매개변수 방정식의 t값)
// x, y, z축의 충돌을 검사하며 점점 좁혀나간다.
float t_min = 0f;
float t_max = 1f;
bool hit = false;
// do while 반복문 영역은 반복을 위한 것이 아니라 조건에 안맞았을 시 바로 빠져나오기 위한 영역.
// while (false)이기 때문에 단 한번만 실행된다.
do
{
// x
float tx_min = 0f;
float tx_max = 1f;
if (sv.x == 0f)
{
// 선분이 x좌표로 이동하지 않는다는 뜻이므로 선분의 위치가 박스영역 안인지만 확인하면 된다.
// 그리고 0으로 나누지 않기 위해서도 따로 처리한다.
if (s0.x < b0.x || s0.x > b1.x) break;
}
else
{
// 선분과 박스 영역의 x값의 매개변수를 구한다.
float tx0 = (b0.x - s0.x) / sv.x;
float tx1 = (b1.x - s0.x) / sv.x;
// x축의 최소값 최대값을 결정
tx_min = Mathf.Min(tx0, tx1);
tx_max = Mathf.Max(tx0, tx1);
// 최소, 최대값이 영역을 벗어났는지 확인
if (tx_max < 0f || tx_min > 1) break;
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * tx0), 0.3f);
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * tx1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
// t_min이 x축의 최대(tx_max)보다 크다는 것은 다른축과 겹치는 영역이 없다는 것이기 때문에 종료한다.
// t_max가 x축의 최소(tx_min)보다 작다는 것은 다른축과 겹치는 영역이 없다는 것이기 때문에 종료한다.
if (t_min > tx_max || t_max < tx_min) break;
// t_min, t_max 값을 tx_min, tx_max 값으로 갱신한다.
// 현재 최소값보다 x축의 최소값이 크면 x축의 최소값으로 갱신한다.(겹치는 영역을 좁혀나간다.)
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, tx_min);
// 현재 최대값보다 x축의 최대값이 크면 x축의 최소값으로 갱신한다.(겹치는 영역을 좁혀나간다.)
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, tx_max);
// 여기서 t_min, t_max 값은 초기값이기 때문에 tx_min, tx_max 을 바로 넣어도 되지만 일관성을 위해 y, z와 똑같이 처리한다.
// y
// x와 똑같이 처리한다.
float ty_min = 0f;
float ty_max = 1f;
if (sv.y == 0f)
{
if (s0.y < b0.y || s0.y > b1.y) break;
}
else
{
float ty0 = (b0.y - s0.y) / sv.y;
float ty1 = (b1.y - s0.y) / sv.y;
ty_min = Mathf.Min(ty0, ty1);
ty_max = Mathf.Max(ty0, ty1);
if (ty_max < 0f || ty_min > 1) break;
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * ty0), 0.3f);
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * ty1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
if (t_max < ty_min || t_min > ty_max) break;
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, ty_min);
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, ty_max);
// z
// x와 똑같이 처리한다.
float tz_min = 0f;
float tz_max = 1f;
if (sv.z == 0f)
{
if (s0.z < b0.z || s0.z > b1.z) break;
}
else
{
float tz0 = (b0.z - s0.z) / sv.z;
float tz1 = (b1.z - s0.z) / sv.z;
tz_min = Mathf.Min(tz0, tz1);
tz_max = Mathf.Max(tz0, tz1);
if (tz_max < 0f || tz_min > 1) break;
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * tz0), 0.3f);
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * tz1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
if (t_max < tz_min || t_min > tz_max) break;
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, tz_min);
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, tz_max);
// 최종 t값이 0~1 사이에 있는지 확인
//hit = !(t_min > 1f || t_max < 0);
hit = (t_min <= 1f && t_max >= 0);
} while (false);
// 선분 그리기
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0, s1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0, s0 + Vector3.up);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s1, s1 + Vector3.up);
// 충돌 영역을 선분에 겹쳐 그린다.
if (hit)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_min), s0 + (sv * t_max));
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_min), s0 + (sv * t_min) + Vector3.up);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_max), s0 + (sv * t_max) + Vector3.up);
}
// 상자 그리기
// 각 축별로 앞위왼 -> 뒤위오 순으로 그린다.
// x축
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b0, new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z), b1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
// y축
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), b0);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z), new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b1, new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
// z축
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b0, new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z), b1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
}
}
AABB 작동화면 캡쳐
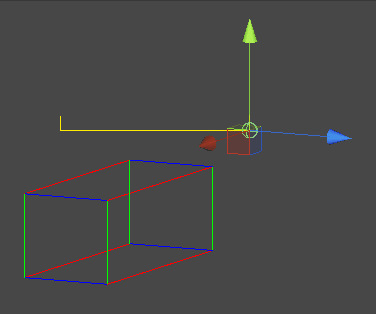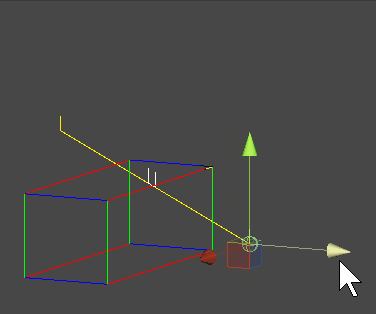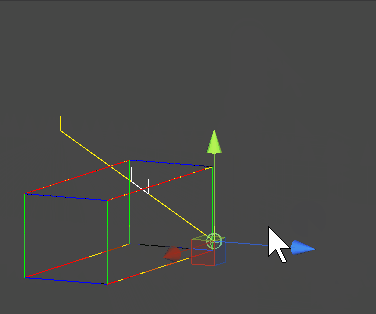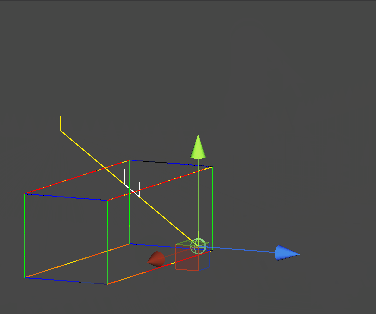
OBB(Oriented Bounding Box)
OBB 바운딩 박스의 정의
- (0, 0) 위치에 있는 크기 1인 기본 상자
- 이 상자의 크기, 회전, 위치를 조절한 변형된 상자가 최종 바운딩 박스
- 데이터 구조는 다음 두 개의 매트릭스로 정의
- 크기, 회전, 위치를 변형시킬 행렬
- 기본 상자의 좌표계로 변형시킬 역행렬
OBB의 충돌 검출 이론
-
바운딩 박스와 충돌 검출할 선분을 바운딩 박스의 원래 좌표계로 변형
- 이 때 바운딩 박스에 저장된 역행렬을 이용한다.
-
변형된 선분과 기본 바운딩 박스의 충돌을 검출
- 충돌 검출에는 AABB 방식을 사용한다.
OBB의 충돌 검출 구현
Matrix4 클래스는 Math - Linear Transformation 포스트 참고
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Segment_OBB_Collision : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform BoxPosition;
public Transform S0; // Segment0
public Transform S1; // Segment1
public float BoundingBoxSize; // Bounding Box Size
public Vector3 Scale = new Vector3(1f, 1f, 1f);
[Range(0, 360)]
public float RotationX = 0f;
[Range(0, 360)]
public float RotationY = 0f;
[Range(0, 360)]
public float RotationZ = 0f;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Vector3 position = new Vector3(0f, 0f, 0f);
float halfSize = BoundingBoxSize / 2;
// 바운딩 박스의 버텍스를 생성한다.
Vector3[] boxVertecis = new Vector3[]
{
new Vector3(position.x - halfSize, position.y- halfSize, position.z- halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x + halfSize, position.y- halfSize, position.z- halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x + halfSize, position.y + halfSize, position.z- halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x- halfSize, position.y + halfSize, position.z- halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x- halfSize, position.y- halfSize, position.z + halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x + halfSize, position.y- halfSize, position.z + halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x + halfSize, position.y+ halfSize, position.z + halfSize),
new Vector3(position.x- halfSize, position.y + halfSize, position.z + halfSize),
};
// 바운딩 박스를 그린다.
Color[] colors = new Color[] { Color.white, Color.green, Color.blue, Color.cyan };
for (int i = 0; i < boxVertecis.Length; i++)
{
Gizmos.color = colors[(uint)i / 2];
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(boxVertecis[i], 0.1f);
}
// 크기 행렬
Matrix4 sm = Matrix4.CreateScale(Scale.x, Scale.y, Scale.z);
// 회전 행렬
Matrix4 rm = Matrix4.CreateRotation(RotationX * Mathf.Deg2Rad, RotationY * Mathf.Deg2Rad, RotationZ * Mathf.Deg2Rad);
// 이동 행렬
Matrix4 tm = Matrix4.CreateTranslation(BoxPosition.position.x, BoxPosition.position.y, BoxPosition.position.z);
// 크기, 회전, 이동 행렬을 조합하여 변환 행렬을 완성한다.
Matrix4 tsr = tm * rm * sm; // 변환 행렬의 적용 순서 반대로 곱해준다.
// 변환 행렬의 역행렬을 구한다.
Matrix4 tsr_inverse = tsr.Inverse(); // 역행렬
// 바운딩 박스의 모든 버텍스에 변환행렬을 곱해준다.
for (int i = 0; i < boxVertecis.Length; i++)
{
boxVertecis[i] = tsr * boxVertecis[i];
}
// 변환된 바운딩 박스를 그린다.
for (int i = 0; i < boxVertecis.Length; i++)
{
Gizmos.color = colors[(uint)i / 2];
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(boxVertecis[i], 0.1f);
}
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[0], boxVertecis[1]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[1], boxVertecis[2]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[2], boxVertecis[3]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[3], boxVertecis[0]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[4], boxVertecis[5]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[5], boxVertecis[6]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[6], boxVertecis[7]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[7], boxVertecis[4]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[0], boxVertecis[4]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[1], boxVertecis[5]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[2], boxVertecis[6]);
Gizmos.DrawLine(boxVertecis[3], boxVertecis[7]);
// 바운딩 박스의 모든 버텍스에 변환행렬의 역행렬을 곱하여 원래 좌표계로 돌아가게 한다.
for (int i = 0; i < boxVertecis.Length; i++)
{
boxVertecis[i] = tsr_inverse * boxVertecis[i];
}
// 바운딩 박스와 충돌 체크할 선분을 바운딩 박스의 원래 좌표계로 변형한다.
Vector3 s0 = tsr_inverse * S0.position;
Vector3 s1 = tsr_inverse *S1.position;
// 원래 좌표계로 돌아간 바운딩 박스와 선분을 충돌 체크한다.
bool hit = HitTest(boxVertecis[0], boxVertecis[6], s0, s1);
// 충돌 체크 여부에 따라 선분의 색을 달리하여 그린다.
Gizmos.color = hit ? Color.red : Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(S0.position, S1.position);
}
bool HitTest(Vector3 b0, Vector3 b1, Vector3 s0, Vector3 s1)
{
Vector3 sv = s1 - s0;
// 선분과 박스의 충돌하는 곳의 최대, 최소값.(직선의 매개변수 방정식의 t값)
// x, y, z축의 충돌을 검사하며 점점 좁혀나간다.
float t_min = 0f;
float t_max = 1f;
bool hit = false;
// do while 반복문 영역은 반복을 위한 것이 아니라 조건에 안맞았을 시 바로 빠져나오기 위한 영역.
// while (false)이기 때문에 단 한번만 실행된다.
do
{
// x
float tx_min = 0f;
float tx_max = 1f;
if (sv.x == 0f)
{
// 선분이 x좌표로 이동하지 않는다는 뜻이므로 선분의 위치가 박스영역 안인지만 확인하면 된다.
// 그리고 0으로 나누지 않기 위해서도 따로 처리한다.
if (s0.x < b0.x || s0.x > b1.x) break;
}
else
{
// 선분과 박스 영역의 x값의 매개변수를 구한다.
float tx0 = (b0.x - s0.x) / sv.x;
float tx1 = (b1.x - s0.x) / sv.x;
// x축의 최소값 최대값을 결정
tx_min = Mathf.Min(tx0, tx1);
tx_max = Mathf.Max(tx0, tx1);
// 최소, 최대값이 영역을 벗어났는지 확인
if (tx_max < 0f || tx_min > 1) break;
//Gizmos.color = Color.red;
//Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * tx0), 0.3f);
//Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * tx1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
// t_min이 x축의 최대(tx_max)보다 크다는 것은 다른축과 겹치는 영역이 없다는 것이기 때문에 종료한다.
// t_max가 x축의 최소(tx_min)보다 작다는 것은 다른축과 겹치는 영역이 없다는 것이기 때문에 종료한다.
if (t_min > tx_max || t_max < tx_min) break;
// t_min, t_max 값을 tx_min, tx_max 값으로 갱신한다.
// 현재 최소값보다 x축의 최소값이 크면 x축의 최소값으로 갱신한다.(겹치는 영역을 좁혀나간다.)
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, tx_min);
// 현재 최대값보다 x축의 최대값이 크면 x축의 최소값으로 갱신한다.(겹치는 영역을 좁혀나간다.)
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, tx_max);
// 여기서 t_min, t_max 값은 초기값이기 때문에 tx_min, tx_max 을 바로 넣어도 되지만 일관성을 위해 y, z와 똑같이 처리한다.
// y
// x와 똑같이 처리한다.
float ty_min = 0f;
float ty_max = 1f;
if (sv.y == 0f)
{
if (s0.y < b0.y || s0.y > b1.y) break;
}
else
{
float ty0 = (b0.y - s0.y) / sv.y;
float ty1 = (b1.y - s0.y) / sv.y;
ty_min = Mathf.Min(ty0, ty1);
ty_max = Mathf.Max(ty0, ty1);
if (ty_max < 0f || ty_min > 1) break;
//Gizmos.color = Color.red;
//Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * ty0), 0.3f);
//Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * ty1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
if (t_max < ty_min || t_min > ty_max) break;
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, ty_min);
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, ty_max);
// z
// x와 똑같이 처리한다.
float tz_min = 0f;
float tz_max = 1f;
if (sv.z == 0f)
{
if (s0.z < b0.z || s0.z > b1.z) break;
}
else
{
float tz0 = (b0.z - s0.z) / sv.z;
float tz1 = (b1.z - s0.z) / sv.z;
tz_min = Mathf.Min(tz0, tz1);
tz_max = Mathf.Max(tz0, tz1);
if (tz_max < 0f || tz_min > 1) break;
//Gizmos.color = Color.red;
//Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(s0 + (sv * tz0), 0.3f);
//Gizmos.DrawWireCube(s0 + (sv * tz1), Vector3.one * 0.55f);
}
if (t_max < tz_min || t_min > tz_max) break;
t_min = Mathf.Max(t_min, tz_min);
t_max = Mathf.Min(t_max, tz_max);
// 최종 t값이 0~1 사이에 있는지 확인
//hit = !(t_min > 1f || t_max < 0);
hit = (t_min <= 1f && t_max >= 0);
} while (false);
// 선분 그리기
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0, s1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0, s0 + Vector3.up);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s1, s1 + Vector3.up);
// 충돌 영역을 선분에 겹쳐 그린다.
if (hit)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.white;
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_min), s0 + (sv * t_max));
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_min), s0 + (sv * t_min) + Vector3.up);
Gizmos.DrawLine(s0 + (sv * t_max), s0 + (sv * t_max) + Vector3.up);
}
// 상자 그리기
// 각 축별로 앞위왼 -> 뒤위오 순으로 그린다.
// x축
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b0, new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z), b1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
// y축
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), b0);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z), new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b1, new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
// z축
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b0.x, b1.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(b0, new Vector3(b0.x, b0.y, b1.z));
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b1.y, b0.z), b1);
Gizmos.DrawLine(new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b0.z), new Vector3(b1.x, b0.y, b1.z));
return hit;
}
}
OBB 작동화면 캡쳐