Direct3D
[TOC]
COM(Component Object Model)
- 응용 프로그램 이진 인터페이스
- 프로그램이나 시스템을 이루는 컴포넌트들이 상호 통신할 수 있도록 하는 메커니즘
- 서로 다른 프로그램들이 서로 통신할 수 있도록 하는 명세
- 컴포넌트란
- .ocx, .dll, .exe를 확장자로 갖는 실행 가능한 바이너리 파일
- 특징
- 언어 독립성
- 서로 다른 언어로 작성된 컴포넌트들이 COM을 지원하는 툴로 만들어졋다면 마치 동일한 개발 도구로 생성한 프로그램 모듈처럼 상호 통신할 수 있다.
- Binary Standard
- 다른 플랫폼으로 작성된 프로그램의 소스코드가 없이 binary 파일만 있어도 사용할 수 있다.
- Version Control
- 새로운 기능을 모듈에 추가할 수 있다.
- 새로운 기능과 이전 기능을 클라이언트 요청에 따라 동시에 제공할 수 있다.
- Location Transparency
- 컴포넌트가 물리적 위치에 관계없이 다른 컴포넌트 혹은 컴포넌트 클라이언트에 의해 사용될 수 있다.
- In-process
- .dll, .ocx
- 컴포넌트 클라이언트의 메모리 영역으로 로드되어 사용됨
- Out-of-process
- .exe
- 컴포넌트 클라이언트와 동일한 머신에서 수행
- Out-of-machine(네트워크를 통한 리모트 머신)
- .exe
- 컴포넌트 클라이언트와 네트워크로 연결된 다른 머신에서 수행
- 언어 독립성
- Interface
- COM이 제공하는 기능
- COM 컴포넌트는 하나 이상의 인터페이스를 제공해야한다.
- COM 객체가 제공하는 기능을 기술한 것
- 바이너리 파일로 배포되는 COM 컴포넌트가 자신이 제공하는 기능을 이를 사용하려는 프로그램에 알려줄 수 있는 방법이 필요하기 때문
Direct3D와 다른 시스템 컴포넌트와의 관계도
- HAL(Hardware Abstraction Layer)
- 하드웨어 추상화 계층
- 컴퓨터의 물리적인 하드웨어와 컴퓨터에서 실행되는 소프트웨어 사이의 추상화 계층
- 하드웨어의 차이를 숨겨서 응용 프로그램이 작동할 수 있는 일관된 플랫폼을 제공
- 하드웨어 가속을 사용하므로 빠르지만 특정 하드웨어에서는 안돌아갈 수 있다.
- Reference Device
- 하드웨어 가속을 하지 않는다.
- 범용적이지만 느리다.
- GDI(Graphics Device Interface)
- 응용프로그램에서 그래픽 관련 하드웨어를 사용할 수 있게 한다.
- Bitmap, Brush, Color, Font, Pen, Video Display, Printer, …
-
DDI(Device Driver Interface)
- 하드웨어 설치 후 운영체제에 설치하는 소프트웨어
- 드라이버
Windows10에서 DirectX SDK 설치
DirectX SDK 9 설치
- 설치 안하고 사용하려 했으나 예제를 따라하기 힘들어 그냥 설치한다.
- https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=6812
- 설치하니 프로그램 목록에 다음 것들이 추가됐다.
- Microsoft DirectX SDK (June 2010)
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable - x86 9.0.30729.17
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable - x86 10.0.30319
- 헤더파일과 라이브러리를 프로젝트에 추가한다.
- 2012 11월 Windows8.0부터 Windows SDK에 DirectX SDK가 포함되어 따로 설치할 필요가 없다.
- 단, 일부 기능이 미지원될 수 있다.
- Windows10에서 DirceX9 SDK를 따로 설치하지 않고 DirectX9을 사용할 수 있지만 기존의 라이브러리중 사용할 수 없는 것이 있다.
- d3dx9math.h
- 여기에서 사용된 D3DXVECTOR3 등의 구조체는 DirectXMath.h에 있는 구조체로 대체하여 사용해야한다.
- 여기에 대응되는 목록이 있다.
- Working with D3DXMath
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/dxmath/pg-xnamath-migration-d3dx
- d3dx9math.h
DirectX9를 설치한 경우
- DirectX 설치 디렉터리의 include 디렉터리 경로를 프로젝트 포함 디렉터리에 추가
- DirectX 설치 디렉터리의 lib 디렉터리 경로를 프로젝트 라이브러리 디렉터리에 추가
- 프로젝트 설정 > 링커 > 추가 종속성에 다음 추가
- dxguid.lib
- d3d9.lib
- d3dx9.lib
Direct3D 초기화 및 생성
//Direct3D 9버전의 헤더 추가
#include <d3d9.h>
//Direct3D 9 라이브러리 추가
//#pragma comment는 프로젝트 속성에서 lib를 포함하지 않아도 사용할 수 있게 한다.
//첫번째 인자는 등록할 확장명, 두번째 인자는 파일 이름
#pragma comment (lib, "d3d9.lib")
//DirectX 시스템 객체 포인터, COM interface이다.
LPDIRECT3D9 g_pD3DInterface;
//DirectX 디바이스 객체(실제 화면을 출력하는 역할)
//디바이스 인터페이스, 그래픽 드라이버, 비디오 카드에 대한 정보를 가지고 있다.
//렌더링을 위해 사용한다.
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 g_pD3DDevice;
//g_pD3DInterface
//Direct3D COM interface를 생성
//Direct3D 9C 버전에서는 32를 리턴한다.
if ((g_pD3DInterface = Direct3DCreate9(D3D_SDK_VERSION)) == nullptr) {
return E_FAIL;
}
//g_pD3DInterface 디바이스 생성에 필요한 파라미터를 전달하고 그래픽 장치에 대한 정보를 받아오는 구조체
D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS sD3DParam;
//sD3DParam의 메모리를 초기화한다.
//참고로 sD3DParam의 기본값은 대부분 0이기 때문에 0으로 초기화하고 필요한 값만 변경하면 된다.
ZeroMemory(&sD3DParam, sizeof(sD3DParam));
//true:창, false:전체화면
sD3DParam.Windowed = true;
//화면 버퍼링 방식 지정
//D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD: 플립방식으로 백버퍼의 값을 보존하지 않는 방식. 따라서 플리핑 시 주소만 교환하므로 빠르다.
//D3DSWAPEFFECT_FLIP: 플립방식으로 백버퍼의 값을 보존하는 방식. 플리핑 시 이전 백 버퍼의 내용을 다음 백버퍼에 복사하고 프론트 버퍼로 지정되므로 느리다. 백버퍼가 여러개일 수 있다.
//D3DSWAPEEFECT_COPY: 백버퍼를 고정하는 방식으로 프론트 버퍼에 백 버퍼의 픽셀을 복사한다.
sD3DParam.SwapEffect = D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD;
//현재 윈도우와 동일한 색상 정보를 갖는 백버퍼를 사용
sD3DParam.BackBufferFormat = D3DFMT_UNKNOWN;
//Direct3D를 사용할 윈도우 핸들
sD3DParam.hDeviceWindow = g_hWnd;
//Direct3D 디바이스 객체를 생성
if (FAILED(g_pD3DInterface->CreateDevice(D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT,
//그래픽 디바이스 타입을 정한다.
//그래픽 가속을 위해 HAL(Hardware Abstraction Layer)를 사용한다.
D3DDEVTYPE_HAL,
//윈도우 핸들
g_hWnd,
//D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING: 3D 계산을 소프트웨어로 한다.
//D3DCREATE_MIXED_VERTEXPROCESSING: 소프트웨어와 하드웨어 분할처리
//D3DCREATE_HARDWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING: 하드웨어에서 처리
D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING,
//D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS의 포인터
&sD3DParam,
//LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9의 포인터(이중포인터)
&g_pD3DDevice))) {
return E_FAIL;
};
//render
//백버퍼를 지정된 색으로 지운다(비운다)
//첫번재, 두번째 매개변수는 사용되지 않는다.
//세번째는 백버퍼를 비워야하므로 D3DCLEAR_TARGET을 지정, D3DCLEAR_TARGET: 백버퍼를 지우겠다는 뜻.
//네번재는 D3DCOLOR_XRGB 매크로를 통해 색을 지정, XRGB는 Alpha값을 안쓴다는 뜻. 255가 1.0이다.
g_pD3DDevice->Clear(0, nullptr, D3DCLEAR_TARGET, D3DCOLOR_XRGB(0, 40, 100), 1.0f, 0);
//g_pD3DInterface에서 비디오 메모리를 컨트롤 하기 위해 잠금을 해지한다.
//용도1. g_pD3DInterface 메모리 컨트롤
//용도2. BeginScene()을 호출하면 메모리에 단독으로 액세스 할 수 있기 때문에 비디오 RAM 버퍼를 잠금 또는 해지할 때 사용
if (SUCCEEDED(g_pD3DDevice->BeginScene())) {
//여기서 화면을 그린다.
//BeginScene()로 잠금해지된 비디오 메모리를 잠근다.
g_pD3DDevice->EndScene();
//백버퍼를 프론트버퍼로 교환(플리핑)한다.
g_pD3DDevice->Present(nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
};
//release g_pD3DInterface
//디바이스를 먼저 해제한다.
if(g_pD3DDevice != nullptr) g_pD3DDevice->Release();
if (g_pD3DInterface != nullptr) g_pD3DInterface->Release();
Direct3D 구조
Direct3D 그래픽 파이프라인 구조
- 입력 조립기
- 정점 셰이더
- 덮개 셰이더
- 테셀레이터
- 영역 셰이더
- 기하 셰이더
- 스트림 출력
- 래스터화
- 픽셀 셰이더
- 출력 병합기
벡터
벡터 구조체
- D3DVECTOR
- x, y, z값만 가지는 단순한 구조체
벡터 구조체 확장
- D3DXVECTOR3
- D3DVECTOR를 상속하여 연산자 오버로딩 등 추가 기능을 더한 구조체
벡터의 연산
- 헤더: D3dx9math.h
- 라이브러리: D3dx9.lib
벡터의 합
- D3DXVec3Add()
- D3DXVECTOR3의 operator+를 사용해도 된다.
벡터의 차
- D3DXVec3Subtract()
- D3DXVECTOR3의 operator-를 사용해도 된다.
벡터의 크기
- D3DXVec3Length()
벡터의 크기 변환
- D3DXVec3Scale()
벡터의 정규화
- D3DXVecNormalize()
벡터의 내적
- D3DXVec3Dot()
벡터의 외적
- 두 벡터로 이루어진 평면이 앞면인지 뒷면인지 판단
- 평면이 법선 벡터와 카메라 시선 벡터의 내적이 양수이면 뒷면 음수이면 앞면
- 빛의 방향과 법선 벡터 사이각의 정도에 따라 빛의 양을 결정
-
내적의 절대값( -1~1 )을 빛의 양에 곱해준다.
-
- 외적은 연산순서가 바뀌면 방향이 다른 벡터가 나오므로 교환법칙이 성립하지 않는다.
- D3DXVec3Cross()
정점
정점
- 공간 상의 한점
- 선분에서는 각 끝에 위치한 점
- 삼각형에서는 각 꼭지점
정점 포맷
- d3d에서 정점을 나타내기 위한 자료구조
- FVF(flexible vertex format)
- 각 프로그램에 맞게 정점 포맷을 정의할 수 있도록 유연성을 제공한다.
- 필요로하는 정점 포맷을 선택하여 조합할 수 있다.
FVF의 요소들
| 이름 | 한글 이름 | 자료구조 | 자료형 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | 정점의 좌표 | x, y, z | float3 | 정점의 3차원 x, y, z 값 |
| RHW(Reciprocal Homogeneous W) | - | RHW | float | 동차 좌표계의 W값(이미 변환된 정점에만 사용하는 옵션) |
| Blending Weight Data | 결합가중치 | 1st-5th Blend Weight | - | 블렌딩값(스키닝에 사용) |
| Vertex Normal | 정점의 법선벡터 | x, y, z | float3 | 정점의 법선벡터(광원처리에 사용) |
| Vertex Point Size | 정점의 포인트 크기 | size | float | 정점의 포인트 크기 |
| Diffuse Color | 확산광 색 | r, g, b, a | DWORD | RGBA(r, g, b, a) 매크로값, 정점의 확산광 색을 나타냄 |
| Specular Color | 반사광 색 | r, g, b, a | DWORD | RGBA(r, g, b, a) 매크로값, 정점의 반사광을 나타냄 |
| Texture Coordinate Set 1~8 | 텍스처 좌표 | 1, 2, 3 or 4 | float, float2, float3 or float4 | 텍스처 좌표값, Direct3D는 8개의 텍스처를 동시에 겹쳐서 사용할 수 있다. (예, 첫 번째 값을 diffuse 맵정보로, 두 번째 값을 법선맵 정보로 설정해서 사용하는 식) |
RHW
- 현재의 정점을 2D 좌표처럼 사용
- RHW가 설정되면 현재의 정점 좌표가 3D 변환인 월드, 뷰, 프로젝션 변환이 적용된 최종 좌표로 판단하므로 x, y 좌표만 참조하여 그대로 화면에 출력한다.
- 일반적으로 w의 값은 1.0로 고정하여 사용
정점 포맷 만들기
- FVF로 정점을 정의하고 Flexible vertex format bits로 각 자료형의 역할이 무엇인지 정의한다.
//정점 구조체 정의
struct SVertex {
float x, y, z, rhw;
DWORD color;
};
//정점 구조체 멤버의 역할 정의
#define D3DFVF_SVertex (D3DFVF_XYZRHW | D3DFVF_DIFFUSE)
정점 3개로 삼각형 만들기
SVertex sVertices[3] = {
{100.0f, 200.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0xffff0000},
{200.0f, 100.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0xff00ff00},
{300.0f, 200.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0xff0000ff}
};
Direct3D의 좌표계
- 왼손 좌표계
정점 데이터의 순서
- 정점 데이터는 시계방향으로 만든다.
- Direct3D는 왼손 좌표계이므로 왼손으로 감싸쥐었을 때 왼손의 검지부터 새끼까지의 손가락이 가리키는 방향으로 버텍스를 그려야 법선 벡터가 엄지손가락 쪽으로 향하게 된다.
정점 버퍼 생성
- 출력할 정점을 저장하는 연속적인 메모리 버퍼
- 정점 버퍼는 비디오 메모리에 정점을 저장하기 때문에 시스템 메모리보다 휠씬 빠르다.
- CreateVertexBuffer()
//버텍스버퍼 생성
LPDIRECT3DVERTEXBUFFER9 pVB;//버텍스버퍼의 인터페이스
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->CreateVertexBuffer(
sizeof(SVertex) * sizeof(sVertices) / sizeof(SVertex),//버텍스크기*개수
D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY,//리소스 사용법을 지정(D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY:어플에서 버텍스버퍼의 쓰기 조작만 수행함을 지정)
D3DFVF_SVertex,//버텍스데이터 사용법
D3DPOOL_DEFAULT,//리소스버퍼를 저장할 시스템, 비디오 메모리를 지정(D3DPOOL_DEFAULT:최적의 메모리를 자동 선택)
&pVB,//반환된 버텍스버퍼를 받을 포인터
nullptr//사용하지 않는 변수, nullptr
);
//버텍스버퍼에 버텍스를 저장하기 위해 잠금
//Lock을 하면 다른 자원이 접근할 수 없게되고 정점을 저장할 메모리 포인터를 반환한다.
void *pVertices;//버텍스를 저장할 메모리의 시작 주소를 받을 변수
pVB->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&pVertices, 0);
memcpy(pVertices, sVertices, sizeof(sVertices));//버텍스버퍼에 버텍스를 메모리 복사
pVB->Unlock();//잠금을 해제
정점을 화면에 출력하여 도형 그리기
- d3dDevice->BeginScene()과 d3dDevice->EndScene() 사이에 정점의 렌더링 코드를 작성한다.
- 정점 데이터 스트림
- http://telnet.or.kr/directx/graphics/programmingguide/gettingstarted/rendering/renderingprimitives/vertexdatastreams.htm
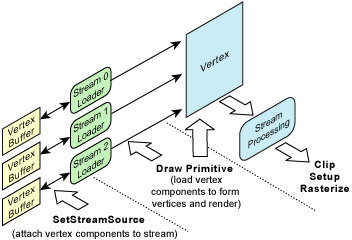
//버텍스 출력
//1. 버텍스버퍼와 버텍스 포맷을 D3D 디바이스에 알려준다. 출력할 버텍스버퍼를 출력 스트림과 연결한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetStreamSource(
0,//0으로 지정
pVertexBuffer, //버텍스버퍼
0, //메모리시작 위치
sizeof(SVertex) //버텍스 크기
);
//2. D3D에 정점 셰이더 정보를 지정, 대부분 FVF만 지정한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetFVF(D3DFVF_SVertex);
//3. 기하 정보를 출력하기 위한 DrawPrimitive() 함수 호출
//DrawIndexedPrimitive(), DrawPrimitiveUP(), DrawIndexedPrimitiveUP()등이 있고
//DrawIndexedPrimitive(), DrawIndexedPrimitiveUP()함수가 게임개발에 많이 사용된다.
//DrawIndexedPrimitive()함수가 가장 빠르다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->DrawPrimitive(
D3DPT_TRIANGLESTRIP,
0, //출력을 시작할 버텍스 인덱스
1 //출력할 개수, 첫번째 파라미터 D3DPRIMITIVETYPE에 영향을 받는다.
);
행렬
행렬 구조체
D3DMATRIX
- 4x4 구조체
- d3d9type.h
D3DXMATRIX, XMMATRIX
- D3DMATRIX를 상속한 클래스
- 연산자 오버로딩 제공
- d3dx9math.h
단위행렬(Identity Matrix) 함수
D3DXMatrixIdentity, XMMatrixIdentity
- 단위행렬을 생성한다.
printTitle("행렬과 단위행렬의 곱");
{
XMMATRIX matMatrix = {
{11, 12, 13, 14},
{21, 22, 23, 24},
{31, 32, 33, 34},
{41, 42, 43, 44},
};
//단위행렬
XMMATRIX matIdentity = XMMatrixIdentity();
//행렬과 단위행렬의 곱 방법1
XMMATRIX matResult = matMatrix * matIdentity;
//행렬과 단위행렬의 곱 방법2
matResult = XMMatrixMultiply(matMatrix, matIdentity);
//출력
printMatrix("matMatrix", matMatrix);
printMatrix("matIdentity", matIdentity);
printMatrix("matResult", matResult);
/*
- matMatrix -
11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0
21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0
31.0 32.0 33.0 34.0
41.0 42.0 43.0 44.0
- matIdentity -
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
- matResult -
11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0
21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0
31.0 32.0 33.0 34.0
41.0 42.0 43.0 44.0
*/
}
전치행렬(Transposed Matrix) 함수
D3DXMatrixTranspose(), XMMatrixTranspose
- 주어진 행렬의 전치행렬을 구한다.
printTitle("전치행렬");
{
XMMATRIX matMatrix = {
{11, 12, 13, 14},
{21, 22, 23, 24},
{31, 32, 33, 34},
{41, 42, 43, 44},
};
//전치행렬
XMMATRIX matTranspose = XMMatrixTranspose(matMatrix);
printMatrix("matMatrix", matMatrix);
printMatrix("matTranspose", matTranspose);
/*
- matMatrix -
11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0
21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0
31.0 32.0 33.0 34.0
41.0 42.0 43.0 44.0
- matTranspose -
11.0 21.0 31.0 41.0
12.0 22.0 32.0 42.0
13.0 23.0 33.0 43.0
14.0 24.0 34.0 44.0
*/
//전치행렬을 다시 전치행렬로 만들기
XMMATRIX matResult = XMMatrixTranspose(matTranspose);
printMatrix("matResult", matResult);
/*
- matResult -
11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0
21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0
31.0 32.0 33.0 34.0
41.0 42.0 43.0 44.0
*/
}
역행렬(Inverse Matrix)
D3DXMatrixInverse(), XMMatrixInverse
- 주어진 행렬의 역행력을 구한다.
- 판별식의 값을 받을 수 있다.
회전행렬
D3DXMatrixRotationX, XMMatrixRotationX
- X축을 기준으로 회전하는 행렬을 구한다.
printTitle("역행렬");
{
XMMATRIX matMatrix;
//회전행렬
XMMATRIX matRotation = XMMatrixRotationX(0.3f);
//행렬식값(0이면 역행렬이 존재하지 않고 0이외의 값이면 역행렬이 존재한다)
XMVECTOR fDeterminant;
//역행렬(회전행렬은 항상 역행렬이 존재)
XMMATRIX matInverse = XMMatrixInverse(&fDeterminant, matRotation);
printMatrix("matRotation", matRotation);
printMatrix("matInverse", matInverse);
printf_s("- fDeterminant : %f\n", fDeterminant.vector4_f32[0]);
/*
- matRotation -
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 0.3 0.0
0.0 -0.3 1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
- matInverse -
1.0 -0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 -0.3 0.0
0.0 0.3 1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
- fDeterminant : 1.000000
*/
//회전행렬과 역행렬의 곱 = 단위행렬
XMMATRIX matResult = XMMatrixMultiply(matRotation, matInverse);
printMatrix("matResult", matResult);
/*
- matResult -
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
}
행 기준, 열 기준(우선)
- 행기준, 열기준은 행렬을 메모리에 어떤 순서로 저장할 것인가에 대한 규칙이다.
- 행 기준(Row Major)
- 11, 12, 13, 14, 21, 22, 23, 24, 31, 32, 33, 34, 41, 42, 43, 44
- 열 기준(Column Major)
- 11, 21, 31, 41, 12, 22, 32, 42, 13, 23, 33, 43, 14, 24, 34, 44
- 행 기준(Row Major)
- 벡터와 행렬의 곱의 순서
- 이것을 행기준, 열기준으로 표현하며 오해가 생겼다.
- “벡터 x 행렬”, “행렬 x 벡터” 이렇게 말해야한다.
- OpenGL
- 곱하는 순서 : “행렬 x 벡터”
- 문맥상 이해하기 어렵다.
- 행렬 곱하기 벡터는 벡터
- 문맥상 이해하기 어렵다.
- 저장 방식 : 열기준
- 행렬 곱하기 벡터에서 행렬을 열기준으로 저장하면 하나의 행을 가져오기 위해 메모리를 한번에 읽을 수 없다.
- 곱하는 순서 : “행렬 x 벡터”
- DirectX
- 곱하는 순서 : “벡터 x 행렬”
- 문맥상 이해하기 쉽다.
- 벡터 곱하기 행렬은 벡터
- 문맥상 이해하기 쉽다.
- 저장 방식 : 행기준
- 곱하는 방식이 벡터 곱하기 행렬인데 행렬이 행기준으로 저장되므로 하나의 열을 한번에 가져올 수 없다.
- 곱하는 순서 : “벡터 x 행렬”
라디안과 호도값 변환 매크로 함수
- D3DXToDegree(radian), XMConvertToDegrees
- 라디안을 호도값으로 변환
- D3DXToRadian(degree), XMConvertToRadians
- 호도값을 라디안으로 변환
printf_s("%f\n", XMConvertToRadians(90) );
//1.570796
printf_s("%f\n", XMConvertToDegrees(3.14) );
//179.908737
선형변환
이동행렬(Translation)
- D3DXMatrixTranslation
- XMMatrixTranslation
XMMATRIX matTranslation = XMMatrixTranslation(10, 20, 30);
printMatrix("matTranslation", matTranslation);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
10.0 20.0 30.0 1.0
*/
크기행렬(Scale)
- D3DXMatrixScaling
- XMMatrixScaling
XMMATRIX matScaling = XMMatrixScaling(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
printMatrix("matScaling", matScaling);
/*
0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.5 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
회전행렬(Rotation)
회전 행렬 함수
- D3DXMatrixRotationX, D3DXMatrixRotationY, D3DXMatrixRotationZ
- XMMatrixRotationX, XMMatrixRotationY, XMMatrixRotationZ
XMMATRIX matRotationX = XMMatrixRotationX(PI);
printMatrix("matRotationX", matRotationX);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -0.0 -1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
x, y, z 축 회전이 적용된 행렬 함수
- D3DXMatrixRotationYawPitchRoll, XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw
- 각 축에 대한 회전행렬을 다음 순서로 곱하여 반환한다.
- Z * X * Y
- 각 축에 대한 회전행렬을 다음 순서로 곱하여 반환한다.
XMMATRIX matRotationRollPitchYaw = XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw(PI, PI, PI);
printMatrix("matRotationRollPitchYaw", matRotationRollPitchYaw);
/*
1.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
-0.0 1.0 -0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
임의의 축을 중심으로 한 회전 행렬 함수
- 임의의 축을 중심으로 시계방향으로 회전한 행렬을 구한다.
- D3DXMatrixRotationAxis, XMMatrixRotationAxis
XMMATRIX matRotationAxis = XMMatrixRotationAxis({1.0, 0, 0,0}, PI);
printMatrix("matRotationAxis", matRotationAxis);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
이동과 회전, 확대/축소 행렬의 결합 순서
- S * R * T
- 크기행렬 * 회전행렬(z->x->y) * 이동 행렬
XMMATRIX matComposite = XMMatrixScaling(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
* XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw(PI, PI, PI)
* XMMatrixTranslation(10, 20, 30);
printMatrix("matComposite", matComposite);
/*
0.5 0.0 -0.0 0.0
-0.0 0.5 -0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0
10.0 20.0 30.0 1.0
*/
쿼터니온(사원수, Quaternion)
- 임의의 축을 기준으로 회전 행렬을 구해주는 수학도구
- 일반 회전 행렬에 비해 계산량이 적다
- 메모리를 적게 차지함
- 짐벌락(Gimbal Lock) 현상이 없음
- 단점
- 직관적인 이해가 어렵다.
쿼터니온 데이터 구조
- x, y, z는 회전축, w는 회전값(라디안)
- 회전 방향은 반시계(CCW)방향
- D3DXQUATERNION, XMVECTOR
쿼터니온 연산
\[Q=q_1 \cdot q_2\]- 행렬 곱셈과 다르게 뒤의 회전이 먼저 적용된다.
- q2 회전을 먼저 적용하고 q1 회전을 적용
- 교환법칙 성립 안됨
회전 행렬을 쿼터니온으로 만드는 함수
- D3DXQuaternionRotationMatrix, XMQuaternionRotationMatrix
printTitle("회전 행렬을 쿼터니온으로 만드는 함수");
{
XMMATRIX matRotation = XMMatrixRotationX(PI);
printMatrix("matRotation", matRotation);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -1.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -0.0 -1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
XMVECTOR vQuaternion = XMQuaternionRotationMatrix(matRotation);
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
*/
}
yaw, pitch, roll에 의한 쿼터니온을 만드는 함수
- D3DXQuaternionRotationYawPitchRoll, XMQuaternionRotationRollPitchYaw
printTitle("yaw, pitch, roll에 의한 쿼터니온을 만드는 함수");
{
XMVECTOR vQuaternion = XMQuaternionRotationRollPitchYaw(PI, PI, PI);
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
-0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
}
임의의 축에 대해서 회전한 쿼터니온을 구하는 함수
- D3DXQuaternionRotationAxis, XMQuaternionRotationAxis
- 회전은 시계방향(CW)
printTitle("임의의 축에 대해서 회전한 쿼터니온을 구하는 함수");
{
XMVECTOR vQuaternion = XMQuaternionRotationAxis({ 1.0, 0, 0, 0 }, PI);
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 -0.0
*/
}
쿼터니온으로부터 회전 행렬을 구하는 함수
- D3DXMatrixRotationQuaternion, XMMatrixRotationQuaternion
printTitle("쿼터니온으로부터 회전 행렬을 구하는 함수");
{
XMVECTOR vQuaternion = XMQuaternionRotationAxis({ 1.0, 0, 0, 0 }, PI);
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 -0.0
*/
XMMATRIX matRotation = XMMatrixRotationQuaternion(vQuaternion);
printMatrix("matRotation", matRotation);
/*
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 -1.0 -0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
*/
}
길이가 1인 쿼터니온을 구하는 함수
- D3DXQuaternionNormalize,
printTitle("길이가 1인 쿼터이온을 구하는 함수");
{
XMVECTOR vQuaternion = { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 };
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
*/
vQuaternion = XMQuaternionNormalize(vQuaternion);
printVector("vQuaternion", vQuaternion);
/*
0.2 0.4 0.5 0.7
*/
}
정점 변환
모델 좌표
- 3D 물체의 기준 좌표
- (0, 0, 0)을 기준으로 하는 정점의 좌표
- 3D 툴에서의 좌표계
정점 렌더링 파이프 라인
월드 변환(World Transformation)
- 모델 좌표를 가진 물체의 정점들을 행렬변환(S * R * T)를 통해 렌더링 공간에 위치시키는 변환
뷰 변환(View Transformation, Camera Transformation)
- 월드 공간의 모든 정점을 이동 및 회전시켜 뷰 공간으로 가져오는 변환
- 뷰(카메라) 좌표로 변환
뷰 변환 행렬
- 뷰를 왼쪽으로 이동하기 위해서는 월드의 모든 정점을 오른쪽으로 이동시켜야한다.
- 카메라(좌표계)가 고정되므로 정점을 이동시켜야한다.
- 스케일 행렬은 없음
투영변환(Projection Transformation)
- 원근 투영으로 가까운 물체와 먼 거리의 물체를 크게 또는 작게 표현하여 원근감이 있게 하는 변환
- 원근법을 적용하여 하나의 면에 정점을 위치시키는 변환
Clipping and Viewport Scaling
- 화면에 안보이는 정점을 제외시킴
- 화면(스크린) 좌표로 변환
변환함수
월드, 뷰, 투영 행렬의 설정
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pD3DDevice = nullptr;//초기화필요
XMMATRIX matTransform;
XMFLOAT4X4 matTransform2;
XMStoreFloat4x4(&matTransform2, matTransform);
pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, (D3DMATRIX*)&matTransform2);
- 모든 모델은 월드변환을 위한 행렬을 각각 보유한다.
뷰 변환 행렬 함수
- D3DXMatrixLookAtLH, XMMatrixLookAtLH
- 뷰 변환 행렬은 일반적으로 하나이다.
inline XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixLookAtLH
(
FXMVECTOR EyePosition, //카메라 위치
FXMVECTOR FocusPosition, //바라보는 방향
FXMVECTOR UpDirection //카메라에서 위쪽으로 향하는 벡터
)
투영 변환 행렬 함수
- D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH, XMMatrixPerspectiveFovLH
inline XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixPerspectiveFovLH
(
float FovAngleY, //시야각
float AspectRatio, //가로세로 비율, height/width
float NearZ, //가까운 면까지 거리
float FarZ // 먼 면까지 거리
)
벡터 변환 행렬 함수
:ballot_box_with_check: 투영변환을 이해한 후 다시 봐야겠다.
D3DXVec3TransformCoord
- 위치 변환 함수
- 3차원 벡터를 w값이 1인 4차원 벡터 (x, y, z, 1)로 만들어 계산한다.
- 4x4 행렬을 곱하여 x, y, z벡터를 구한다.
D3DXVec3TransformNormal
- 벡터 변환 함수
- 벡터를 (x, y, z, 0)으로 만들어 변환 연산을 한다.
- 반환된 값을 정규화해야 크기와 방향을 갖게 된다.
- 로컬 공간에서의 벡터에 회전 및 스케일 변환을 적용하고자 했을 때 월드 공간에서의 벡터를 의미
D3DXVec4Transform
- w값을 임의로 설정하는 함수
- w값을 1로 하면 Coord와 같고 0으로 하면 Normal과 같아진다.
깊이 버퍼 설정
- 깊이 버퍼를 사용하기 위한 D3D 설정
//D3D 파라미터의 z버퍼 설정
sD3DParam.EnableAutoDepthStencil = true;
sD3DParam.AutoDepthStencilFormat = D3DFMT_D24S8;
//디바이스의 z버퍼 설정
pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, true);
//렌더링 설정, D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER 추가
pD3DDevice->Clear(0, nullptr, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER, D3DCOLOR_XRGB(0, 40, 100), 1.0f, 0);
뷰포트 설정
//Viewport
D3DVIEWPORT9 d3dViewport9 = {};
d3dViewport9.X = 0;//렌더링타겟 표면에서 뷰포트가 시작될 x위치
d3dViewport9.Y = 0;//렌더링타겟 표면에서 뷰포트가 시작될 y위치
d3dViewport9.Width = 800;//렌더링타겟에서 출력될 가로 크기
d3dViewport9.Height = 800;//렌더링타겟에서 출력될 세로 크기
d3dViewport9.MinZ = 0.0;//깊이버퍼의 최소 범위
d3dViewport9.MaxZ = 1.0;//깊이버퍼의 최대 범위
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetViewport(&d3dViewport9);
렌더링 파이프라인 만들기
- D3D 디바이스에 변환 행렬 적용
- 정점 변환 행렬
- 월드 변환 행렬 적용
- pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44)
- 뷰 변환 행렬 적용
- pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_VIEW, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44);
- 투영 변환 행렬 적용
- pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_PROJECTION, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44);
- 월드 변환 행렬 적용
- 변환 행렬 적용에 순서는 없음.
- 월드 변환 행렬은 모델마다 다르지만 뷰, 투영 변환 행렬은 모델들이 공유하기 때문에 한번만 만들고 계속 사용할 수 있음.
- 정점 변환 행렬
- 정점을 그릴 수 있게 정보 설정
- 정점 버퍼에 저장된 정점 버퍼와 정점 포맷을 D3D 디바이스에 알림
- pD3DDevice->SetStreamSource
- 정점 데이터를 해석하는 방법을 D3D 디바이스에 알림
- pD3DDevice->SetFVF(D3DFVF_SVertex);
- SetStreamSource에 의해 지정된 정점 버퍼의 정점을 그림
- 정점 버퍼에 저장된 정점 버퍼와 정점 포맷을 D3D 디바이스에 알림
//World transformation
XMMATRIX matWorld = XMMatrixScaling(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)//크기행렬
*XMMatrixRotationX(0.0)//회전행렬
*XMMatrixTranslation(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);//이동행렬
XMFLOAT4X4 f44;
XMStoreFloat4x4(&f44, matWorld);
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44);
//View transformation
XMMATRIX matView = XMMatrixLookAtLH(
{ 10.0, 10.0, -10.0 },//카메라 위치
{ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 },//바라보는 방향
{ 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 }//카메라에서 위쪽으로 향하는 벡터
);
XMStoreFloat4x4(&f44, matView);
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_VIEW, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44);
//Projection trasformation(직교투영)
XMMATRIX matProj = XMMatrixOrthographicLH(
50.0,
50.0,
1.0,//가까운 면의 Z값(음수를 넣으니 WM_SYSCOLORCHANGE가 계속와서 프로그램 진행이 안됨)
100.0//먼 면의 Z값
);
XMStoreFloat4x4(&f44, matProj);
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_PROJECTION, (D3DMATRIX*)&f44);
//정점 출력
//1. 버텍스버퍼와 버텍스 포맷을 D3D 디바이스에 알려준다. 출력할 버텍스버퍼를 출력 스트림과 연결한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetStreamSource(
0,//0으로 지정
pAxisVertexBufferInterface, //버텍스버퍼
0, //메모리시작 위치
sizeof(SVertex) //버텍스 크기
);
//2. D3D에 정점 데이터를 어떻게 해석해하는지 설정한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetFVF(D3DFVF_SVertex);
//3. 기하 정보를 출력하기 위한 DrawPrimitive() 함수 호출
//DrawIndexedPrimitive(), DrawPrimitiveUP(), DrawIndexedPrimitiveUP()등이 있고
//DrawIndexedPrimitive(), DrawIndexedPrimitiveUP()함수가 게임개발에 많이 사용된다.
//DrawIndexedPrimitive()함수가 가장 빠르다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->DrawPrimitive(
D3DPT_LINELIST,
//D3DPT_TRIANGLESTRIP,
0, //출력을 시작할 버텍스 인덱스
3 //출력할 개수, 첫번째 파라미터 D3DPRIMITIVETYPE에 영향을 받는다.
);
인덱스 버퍼
- 정점 버퍼에 들어간 정점의 인덱스를 이용하여 삼각형을 그릴 수 있게 인덱스를 활용하는 버퍼
- LP
정점과 인덱스 선언
- 인덱스는 WORD형으로 나열하며 삼각형은 시계(CW)방향으로 정점의 인덱스를 구성
//정육면체 정점
SVertex2 sCubeVertices[8] = {
{ {-10.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f}, 0xffffffff},
{ {-10.0f, 10.0f, 0.0f}, 0xffff0000},
{ {10.0f, 10.0f, 0.0f}, 0xff00ff00},
{ {10.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f}, 0xff00ff},
{ {-10.0f, -10.0f, 20.0f}, 0xffffffff},
{ {-10.0f, 10.0f, 20.0f}, 0xffff0000},
{ {10.0f, 10.0f, 20.0f}, 0xff00ff00},
{ {10.0f, -10.0f, 20.0f}, 0xff0000ff},
};
//정육면체 인덱스, 면의 방향이 바깥을 향하도록 시계방향으로 그린다.
WORD sCubeIndices[36] = {
//앞
0, 1, 2,
0, 2, 3,
//뒤
7, 6, 5,
7, 5, 4,
//좌
4, 5, 1,
4, 1, 0,
//우
3, 2, 6,
3, 6, 7,
//상
1, 5, 6,
1, 6, 2,
//하
3, 7, 4,
3, 4, 0,
};
정점 버퍼 및 인덱스 버퍼 생성
//버텍스버퍼 생성
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->CreateVertexBuffer(
sizeof(sCubeVertices),//버텍스배열의 크기
D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY,//리소스 사용법을 지정(D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY:어플에서 버텍스버퍼의 쓰기 조작만 수행함을 지정)
D3DFVF_SVertex,//버텍스 타입
D3DPOOL_DEFAULT,//리소스버퍼를 저장할 시스템, 비디오 메모리를 지정(D3DPOOL_DEFAULT:최적의 메모리를 자동 선택)
&pCubeVertexBufferInterface,//반환된 버텍스버퍼를 받을 포인터
nullptr//사용하지 않는 변수, nullptr
);
//버텍스버퍼에 버텍스를 저장하기 위해 잠금
//Lock을 하면 다른 자원이 접근할 수 없게되고 정점을 저장할 메모리 포인터를 반환한다.
void *pVertices;//버텍스를 저장할 메모리의 시작 주소를 받을 변수
pCubeVertexBufferInterface->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&pVertices, 0);
memcpy(pVertices, sCubeVertices, sizeof(sCubeVertices));//버텍스버퍼에 버텍스를 메모리 복사
pCubeVertexBufferInterface->Unlock();//잠금을 해제
//인덱스버퍼 생성
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->CreateIndexBuffer(
sizeof(sCubeIndices),//인덱스배열의 크기
D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY,//리소스 사용법을 지정(D3DUSAGE_WRITEONLY:어플에서 버텍스버퍼의 쓰기 조작만 수행함을 지정)
D3DFMT_INDEX16,//인덱스 타입
D3DPOOL_DEFAULT,//리소스버퍼를 저장할 시스템, 비디오 메모리를 지정(D3DPOOL_DEFAULT:최적의 메모리를 자동 선택)
&pCubeIndexedBufferInterface,//반환된 인덱스버퍼를 받을 포인터
nullptr//사용하지 않는 변수, nullptr
);
//인덱스버퍼에 인덱스를 저장하기 위해 잠금
//Lock을 하면 다른 자원이 접근할 수 없게되고 인덱스를 저장할 메모리 포인터를 반환한다.
void *pIndices;//인덱스를 저장할 메모리의 시작 주소를 받을 변수
pCubeIndexedBufferInterface->Lock(0, sizeof(sCubeIndices), (void**)&pIndices, 0);
memcpy(pIndices, sCubeIndices, sizeof(sCubeIndices));//인덱스버퍼에 인덱스를 메모리 복사
pCubeIndexedBufferInterface->Unlock();//잠금을 해제
정점 버퍼 및 인덱스 버퍼 입력
//버텍스버퍼 입력
//버텍스버퍼와 버텍스 포맷을 D3D 디바이스에 알려준다. 출력할 버텍스버퍼를 출력 스트림과 연결한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetStreamSource(
0,//0으로 지정
pCubeVertexBufferInterface, //버텍스버퍼
0, //메모리시작 위치
sizeof(SVertex2) //버텍스 크기
);
//인덱스버퍼 입력
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetIndices(pCubeIndexedBufferInterface);
인덱스를 이용한 출력(DrawIndexedPrimitive)
- 정점 버퍼만 사용할 경우 DrawPrimitive() 함수를 사용했지만 인덱스 버퍼를 사용할 경우 DrawIndexedPrimitive() 함수를 사용한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->DrawIndexedPrimitive(
D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST,
0,//정점버퍼의 시작인덱스 오프셋. 만약 1일 경우 인덱스 버퍼의 0값이 정점 버퍼의 1인덱스를 가리킨다.
0,//정점버퍼의 최소인덱스. 만약 1일 경우 0번 정점은 사용되지 않는다.
8,//그려질 정점의 개수, BaseVertexIndex + MinIndex 만큼 빼주면 된다.
0,//인덱스버퍼의 시작인덱스 오프셋. 만약 1일 경우 1번 인덱스버퍼부터 그린다.
12//그려질 도형(삼각형)의 개수
);
컬링에 관한 설정
- 와이어프레임과 같이 컬링을 하지 않아야하는 경우
//렌더링하기 전 컬링을 하지 않도록 설정한다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_CULLMODE, D3DCULL_NONE);
//렌더링 후 컬링을 다시 켜준다
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_CULLMODE, D3DCULL_CCW);
SIMD(Single Instruction Multiple Data)
- 하나의 명령어로 여러 개의 값을 동시에 계산하는 방식
- 벡터 프로세서에서 많이 사용되는 방식으로, 비디오 게임 콘솔이나 그래픽 카드와 같은 멀티미디어 분야에 자주 사용된다.
- 인텔의 MMX(SSE2), 스트리밍 SIMD 확장(SSE), AMD의 3D 나우 등에서 이를 적용했다.
- 구현법
- Intrinsic Function 이용
- Intrinsic Function
- 모양은 함수와 같지만 어셈블리 명령어와 1:1로 매칭되어 좀 더 쉽게 SSE를 이용할 수 있게 해주는 내장 함수
- Intrinsic Function
- 정렬된 메모리 사용(aligned memory)
- 메모리의 시작점을 align한 숫자의 배수로 맞추고, 내부 원소의 크기를 align한 크기로 맞추는 것
- Intrinsic Function 이용
도형
- D3DX에서 도형 제공
- 박스, 원기둥, 구, 주전자, 텍스트, 토러스, 폴리건
메쉬
- 정점들로 물체를 표현한 것
- 물체를 표현하기 위한 정점 집합
- LPD3DXMESH 타입으로 사용한다.
- 필요한 헤더와 라이브러리
- D3dx9shape.h
- D3dx9.lib
도형 생성 함수
- 메쉬를 생성하기 위한 함수
박스
HRESULT WINAPI
D3DXCreateBox(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice, //D3DDevice
FLOAT Width,
FLOAT Height,
FLOAT Depth,
LPD3DXMESH* ppMesh,
LPD3DXBUFFER* ppAdjacency//nullptr
);
구
HRESULT WINAPI
D3DXCreateSphere(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice,
FLOAT Radius, //반지름
UINT Slices, //구를 나누는 선분의 개수
UINT Stacks, //선분으로 나누어진 영역을 90도 방향으로 나누는 개수
LPD3DXMESH* ppMesh,
LPD3DXBUFFER* ppAdjacency//nullptr
);
주전자
HRESULT WINAPI
D3DXCreateTeapot(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice,
LPD3DXMESH* ppMesh,
LPD3DXBUFFER* ppAdjacency
);
원기둥
HRESULT WINAPI
D3DXCreateCylinder(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice,
FLOAT Radius1, //윗면 원의 반지름
FLOAT Radius2, //아랫면 원의 반지름
FLOAT Length, //높이
UINT Slices, //원을 나누는 개수
UINT Stacks, //원을 나눈뒤 생기는 원기둥의 면을 나누는 개수
LPD3DXMESH* ppMesh,
LPD3DXBUFFER* ppAdjacency);
도형 출력 함수
- LPD3DXMESH의 멤버 함수 DrawSubset()을 이용한다.
- 법선벡터를 이용하여 라이팅 계산을 하지 않을 경우 라이트를 끄지 않으면 검게 출력된다.
- 월드 변환이 적용되지 않았으므로 바로 출력하면 (0,0,0) 좌표에 출력된다.
HRESULT __stdcall DrawSubset(
DWORD AttribId //그리려는 서브셋 번호를 지정. 모든 삼각형을 그릴 경우 0.
);
지형 그리기
정점 만들기
- 좌상단부터 차례대로 정점을 만들어 저장한다.
인덱스 버퍼 생성
삼각형 그리는 순서
- 정점들이 만드는 사각형의 좌상단 점을 공유하는 삼각형 두개를 그린다.
- 우상단 정점을 공유하는 방식보다 로직이 좀 더 간단해진다.
- 왼손 좌표계에서는 시계방향(CW)으로 삼각형을 그린다.
버텍스 개수로 삼각형 개수 구하기
//지형 버텍스 생성, 행과 열로 생성한다.
int iTerrainVertexCount = iTerrainVertexRow * iTerrainVertexCol;
vTerrainVertices = new SVertex[iTerrainVertexCount];
for (size_t i = 0; i < iTerrainVertexCount; i++)
{
int iRow = i / iTerrainVertexCol;
int iCol = i % iTerrainVertexCol;
//평평한 지형
//vTerrainVertices[i] = { (float)iCol * fTerrainTriangleScale, 0.0f, (float)iRow * -fTerrainTriangleScale, 0xffffffff };
//가운데가 솟아오른 지형
vTerrainVertices[i] = { (float)iCol * fTerrainTriangleScale,
-(sin(D3DX_PI * 2.0f / iTerrainVertexCount * i + D3DX_PI * 0.5f)) * fTerrainHeight + fTerrainHeight,
(float)iRow * -fTerrainTriangleScale, 0xffffffff };
}
//버텍스인덱스 생성
//방법1. 좌상에서 우하로 나뉘는 삼각형
//이 방식의 장점은 사각형 단위로 그리기 때문에 로직이 단순하다.
int iIndicesCount = iTriangleCount * 3;
vTerrainIndices = new WORD[iIndicesCount];
for (size_t i = 0; i < iTriangleCount; i+=2)
{
int iTriangleRow = i / iTriangleColCount;//현재 삼각형의 행번호
int iVerticesIndex = iTriangleRow + i / 2;
int iIndicesIndex = i * 3;
//↘←↑
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex] = iVerticesIndex;
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex + 1] = iVerticesIndex + 1 + iTerrainVertexCol;
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex + 2] = iVerticesIndex + iTerrainVertexCol;
//→↓↖
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex + 3] = iVerticesIndex;
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex + 4] = iVerticesIndex + 1;
vTerrainIndices[iIndicesIndex + 5] = iVerticesIndex + 1 + iTerrainVertexCol;
}
문자 출력
- 폰트 생성
- D3DXCreateFont() 함수 사용
- 텍스트 출력
- LPD3DXFONT->DrawText() 함수 사용
사운드
FMOD 설치
- fmod.com
- FMOD Studio API 다운
- 설치
- C:\Program Files (x86)\FMOD SoundSystem\FMOD Studio API Windows
FMOD 프로젝트 설정
- FMOD 헤더 및 라이브러리 경로 등록
- 프로젝트 설정 > C/C++ > 일반 > 추가 포함 디렉터리
- ..\FMOD\core\inc;
- 프로젝트 설정 > C/C++ > 링커 > 입력 > 추가 종속성
- ..\FMOD\core\lib\x86\fmod_vc.lib;
- 프로젝트 설정 > C/C++ > 일반 > 추가 포함 디렉터리
- FMOD 사운드 DLL 파일 복사
- ..\FMOD\core\lib\x86\fmod.dll 파일을 실행파일과 같은 디렉터리로 복사
FMOD 사용
초기화
static FMOD_SYSTEM *g_fmodSystem;
FMOD_System_Create(&g_fmodSystem);
FMOD_System_Init(g_fmodSystem, 32, FMOD_INIT_NORMAL, nullptr);
사운드 객체 생성과 사운드 로딩
FMOD_SOUND *fmodSound;//사운드 파일과 일대일 대응
FMOD_System_CreateSound(g_fmodSystem, "sound.mp3",
//FMOD_DEFAULT = FMOD_LOOP_OFF | FMOD_2D | FMOD_HARDWARE
//FMOD_LOOP_NORMAL : 배경음과 같이 반복이 필요할 경우
FMOD_DEFAULT,
0, &fmodSound);
사운드 제어
- 로딩된 사운드는 채널을 통해 출력
- 채널을 FMOD 시스템 초기화 시 설정된 값으로 생성된 채널 중 하나를 반환해준다.
- ? 확인 요.
- 채널을 해제할 필요가 없다.
- 채널을 FMOD 시스템 초기화 시 설정된 값으로 생성된 채널 중 하나를 반환해준다.
- 배경음과 같이 계속 재생돼야하는 사운드는 채널을 저장했다가 컨트롤하고 효과음 등은 채널 변수를 지역변수로 사용하고 버린다.
- 출력 사운드의 데이터 갱신
- FMOD에서 사운드 파일은 스트리밍 방식으로 재생된다.
- 재생되는 일정 데이터만 메모리에 올리고 재생하기 때문에 다음 데이터를 가져오도록 업데이트를 해줘야한다.
- FMOD에서 사운드 파일은 스트리밍 방식으로 재생된다.
FMOD_SYSTEM *pFmodSystem;
FMOD_SOUND *pFmodSound;//사운드 파일과 일대일 대응
FMOD_CHANNEL *pFmodChannel;
//사운드 재생
FMOD_System_PlaySound(g_fmodSystem, fmodSound, nullptr, false, &fmodChannel);
//사운드 종료
FMOD_Channel_Stop(fmodChannel);
//사운드 볼륨 조정
FMOD_Channel_SetVolume(fmodChannel, 0.1f/*0~1*/);
//사운드 스트리밍 데이터 갱신
FMOD_System_Update(fmodSystem);
//사운드 해제
if (pFmodSound) {
FMOD_Sound_Release(pFmodSound);
}
//FMOD 해제
if (pFmodSystem) {
FMOD_System_Close(pFmodSystem);
FMOD_System_Release(pFmodSystem);
}
사운드 리소스
- http://soundbible.com/
- 회원가입 없이 다운 받을 수 있다.
충돌
메쉬에서 경계구 산출하기
- 매개변수로 전달한 메쉬를 감싸는 경계구를 계산해준다.
D3DXVECTOR3 vCenter;
float fRadius;
D3DXVECTOR3 *pVertices;
pSphereMesh->LockVertexBuffer(D3DLOCK_READONLY, (LPVOID*)&pVertices);
pSphereMesh->UnlockVertexBuffer();
D3DXComputeBoundingSphere(pVertices, pSphereMesh->GetNumVertices(),
pSphereMesh->GetNumBytesPerVertex()/*or D3DXGetFVFVertexSize()*/,
&vCenter, &fRadius);
경계 구를 이용한 충돌
- 두 구의 반지름의 합이 두 구의 원점 사이의 거리보다 작거나 같을 경우 충돌로 판정
- 구로 감싸면 빈틈이 많기 때문에 1차 충돌검출에 많이 사용된다.
메쉬에서 경계박스 산출하기
- 매개변수로 전달한 메쉬를 감싸는 경계구를 계산해준다.
//mesh
D3DXCreateTeapot(pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice, &m_pMesh, nullptr);
//bounding box
D3DXVECTOR3 *pVertices;
m_pMesh->LockVertexBuffer(D3DLOCK_READONLY, (LPVOID*)&pVertices);
D3DXComputeBoundingBox(pVertices, m_pMesh->GetNumVertices(),
m_pMesh->GetNumBytesPerVertex(), &m_vBoundingBoxMin, &m_vBoundingBoxMax);
경계 박스를 이용한 충돌
방법1. 겹치는 영역이 있는지 확인
- 장점
- 로직이 간단하다.
- 한번에 겹치는 영역이 있는지 확인할 수 있다.
- 박스가 다른 박스를 포함하더라도 충돌여부를 판단할 수 있기 때문에 함수를 두 번 호출하지 않아도 된다.
bool CheckCollision(const D3DXVECTOR3 &vMin0, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMax0, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMin1, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMax1) {
return vMin0.x <= vMax1.x && vMax0.x >= vMin1.x &&
vMin0.y <= vMax1.y && vMax0.y >= vMin1.y &&
vMin0.z <= vMax1.z && vMax0.z >= vMin1.z;
}
//check collision
bColided = CheckCollision1(vMin0, vMax0, vMin1, vMax1);
방법2. 박스의 꼭지점이 다른 박스 안에 있는지 확인
- 단점
- 모든 꼭지점을 조사해야한다.
- 상대 박스에 포함되는지 각각 조사애햐하기 때문에 함수를 두번 호출해야한다.
- 이렇게 할 수도 있다라고만 생각하고 쓰면 안되겠다.
bool CheckCollision(const D3DXVECTOR3 &vMin0, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMax0, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMin1, D3DXVECTOR3 &vMax1) {
D3DXVECTOR3 vDistance = vMax0 - vMin0;
bool bColided = false;
D3DXVECTOR3 vPoint = {};
//min
vPoint = vMin0;//left down
bColided = CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMin0.x, vMin0.y + vDistance.y, vMin0.z };//left up
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMin0.x + vDistance.x, vMin0.y + vDistance.y, vMin0.z };//right up
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMin0.x + vDistance.x, vMin0.y, vMin0.z };//right down
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
//max
vPoint = vMax0;//right up
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMax0.x, vMax0.y - vDistance.y, vMax0.z };//right down
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMax0.x - vDistance.x, vMax0.y - vDistance.y, vMax0.z };//left down
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
vPoint = { vMax0.x - vDistance.x, vMax0.y, vMax0.z };//left up
bColided = bColided || CheckPointInBox(vPoint, vMin1, vMax1);
return bColided;
}
//check collision
bColided = CheckCollision0(vMin0, vMax0, vMin1, vMax1);
bColided = bColided || CheckCollision0(vMin1, vMax1, vMin0, vMax0);
사각형과 원의 충돌 검출(내 생각)
- 사각형을 감싸는 원과 충돌 여부
- 거리의 제곱과 비교하여 최적화한다.
- 사각형의 중심과 원의 중심을 잊는 벡터와 만나는 사각형의 선분과 원의 방정식을 풀었을 때 해가 1개 혹은 2개인지 여부
- 원의 중심이 사각형 안에 있는지 여부
- 사각형의 중심과 원의 중심을 잊는 벡터와 원의 둘레가 만나는 점이 사각형 안에 있는지 여부
- 이 방법은 사각형의 꼭지점이 원과 먼저 만날 수 있으므로 정확한 계산을 할 수 없다.
머티리얼
- 각 물체에 빛이 닿았을 때 물체의 표면으로부터 반사되는 색상을 설정
D3DMATERIAL9 구조체
typedef struct _D3DMATERIAL9 {
D3DCOLORVALUE Diffuse; /* Diffuse color RGBA */
D3DCOLORVALUE Ambient; /* Ambient color RGB */
D3DCOLORVALUE Specular; /* Specular 'shininess' */
D3DCOLORVALUE Emissive; /* Emissive color RGB */
float Power; /* Sharpness if specular highlight */
} D3DMATERIAL9;
//머티리얼 설정
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetMaterial(&material);
- Diffuse
- 빛이 물체에 닿았을 경우에 반사하는 색상 설정
- Ambient
- 방향성이 없는 빛에 대한 반사색을 설정
- 방향성(Direction Light) 빛에 의한 반사색에는 영향을 주지 않음
- Specular
- 빛에 의한 밝은 부분의 반사색보다 반짝이게 하는 색상 설정(HighLight의 색상을 설정)
- Emissive
- 재질이 스스로 특정 색을 방출하는 옵션
- Power
- 스페큘러 하이라이트의 선명도를 지정하는 부동 소수점값
- 값이 높아짐에 따라 하이라이트 부분이 보다 선명하게 된다.
라이트
주변광(Ambient Light)
- 모든 장소에 동일한 세기로 비추어지는 빛
- 위치나 방향이 없고 색상과 강도만 있으므로 음영 효과가 생기지 않음
포인트광(Point Light)
- 광원의 위치를 기반으로 빛이 퍼져나가는 빛
- 라이트의 위치와 멀어지면 멀어질 수록 표면에 닿는 빛의 강도가 약하게 표현되는 특징이 있다.
- 백열전구와 비슷하다.
방향광(Directional Light)
- 색상과 방향은 가지지만 라이트 위치는 가지지 않는다.
- 거리와는 상관없이 일정하게 비추는 효과
스포트라이트(Spot Light)
- 색상, 위치, 빛에 대한 방향을 가짐
- 계산량이 상당히 많아서 게임에서는 거의 사용되지 않고 시뮬레이션 분야와 같이 사실감을 극대와해야하는 그래픽스 분야에서 사용됨
라이트의 속성
Ambient
- 빛을 직접 받지 않는 곳의 주변색을 설정
Diffuse
- 라이트가 비추는 빛의 색상
라이트 구조체
typedef struct _D3DLIGHT9 {
D3DLIGHTTYPE Type; /* Type of light source */
D3DCOLORVALUE Diffuse; /* Diffuse color of light */
D3DCOLORVALUE Specular; /* Specular color of light */
D3DCOLORVALUE Ambient; /* Ambient color of light */
D3DVECTOR Position; /* Position in world space */
D3DVECTOR Direction; /* Direction in world space */
float Range; /* Cutoff range */
float Falloff; /* Falloff */
float Attenuation0; /* Constant attenuation */
float Attenuation1; /* Linear attenuation */
float Attenuation2; /* Quadratic attenuation */
float Theta; /* Inner angle of spotlight cone */
float Phi; /* Outer angle of spotlight cone */
} D3DLIGHT9;
typedef enum _D3DLIGHTTYPE {
D3DLIGHT_POINT = 1,
D3DLIGHT_SPOT = 2,
D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL = 3,
D3DLIGHT_FORCE_DWORD = 0x7fffffff, /* force 32-bit size enum */
} D3DLIGHTTYPE;
- Type
- 광원의 종류
- D3DLIGHT_POINT, D3DLIGHT_SPOT, D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL, D3DLIGHT_FORCE_DWORD
- Diffuse
- Light가 방사하는 색생
- Specular
- Light가 방사하는 반사색
- Ambient
- Light가 방사하는 주변색
- Direction
- 빛의 방향을 D3DVECTOR 구조체로 설정
- Directional Light, Spot Light의 경우에만 적용됨
라이트 설정
HRESULT SetLight(DWORD Index, const D3DLight9 *pLight);
HRESULT LightEnable(DWORD LightIndex, BOOL bEnable);
법선벡터와 라이트
- 라이트가 적용되려면 법선벡터가 필요하다.
텍스쳐
- 텍스쳐 : 이미지
- bmp, tga, dds, jpg, png
- 가로, 세로 크기가 16의 배수가 돼야한다.
- 텍셀 : 이미지 픽셀
- 텍스쳐 좌표
- 실제 이미지의 크기와 상관없이 상대좌표로 지정한다.
- 가로(tu), 세로(tv)인 0.0f부터 1.0f까지 지정
- 좌하단이 (0,0)이고 우상단이 (1,1)
텍스쳐 정점 구조
//텍스쳐는 항상 D3DFVF_TEX1부터 시작, D3DFVF_TEX0은 사용할 텍스쳐 좌표계가 없다는 것을 알린다.
#define D3DFVF_SVertexTexture (D3DFVF_XYZ | D3DFVF_TEX1)
struct SVertexTexture {
D3DXVECTOR3 xyz;
float tu, tv;
};
텍스쳐 생성
- 외부로부터 이미지를 읽어 텍스쳐 객체인 IDirect3DTexture9을 생성
//텍스쳐 생성
LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9 m_pTexture;
D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice, "../Resources/Textures/darkbrown.png", &m_pTexture);
//등록
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetTexture(0, m_pTexture);
메쉬
x 파일 형식
- x 파일
- x 파일에는 애니메이션, 텍스쳐, 머티리얼, 라이트 등과 같은 많은 정보가 저장
- template이라는 태그를 통해서 구분
- DirectX에서 지원
- 머티리얼이 여러개 있을 수 있고 머티리얼 마다 정점이 각각 있다.
- ase 파일
x 파일 객체와 선언
//x파일을 로드할 때 생성되는 데이터들
LPD3DXMESH m_pMesh;
D3DMATERIAL9 *m_pMeshMaterials;//머티리얼은 여러개가 있을 수 있기 때문에 포인터 변수로 받는다.
LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9 *m_pMeshTextures;
DWORD m_dwNumMaterials;//머티리얼의 개수
x파일 로딩
- 3D Max에서는 머티리얼을 MeshMaterialList라는 템플리트안에 저장하며 각 머티리얼로 구분하여 메쉬가 저장된다.
- 이를 읽고 파싱해주는 함수가 D3DXLoadMeshFromX() 함수이다.
HRESULT WINAPI
D3DXLoadMeshFromXA(
LPCSTR pFilename, //x파일 파일명
DWORD Options, //메쉬를 생성할 메모리,
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pD3DDevice, //Direct3D의 device
LPD3DXBUFFER *ppAdjacency,//인접 정점의 정보를 리턴, directx9에서는 사용하지 않는다.
LPD3DXBUFFER *ppMaterials, //머티리얼 정보를 리턴
LPD3DXBUFFER *ppEffectInstances, //effect의 초기값 리턴, directx9에서는 사용하지 않는다.
DWORD *pNumMaterials,//머티리얼 개수 리턴
LPD3DXMESH *ppMesh//생성된 메쉬 객체를 리턴(정점 정보를 가진 버퍼)
);
//x파일 로드
LPD3DXBUFFER pD3DXMtrlBuffer;//범용적인 데이터를 다룬는 객체, 형 변환이 필수
//pD3DXMtrlBuffer->GetBufferPointer();
//pD3DXMtrlBuffer->GetBufferSize();
D3DXLoadMeshFromX("../Resources/Meshes/Tiger/tiger.x",
D3DXMESH_SYSTEMMEM, //D3DXMESH_MANAGED, D3DXMESH_DYNAMIC
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice,
nullptr,
&pD3DXMtrlBuffer,
nullptr,
&m_dwNumMaterials,
&m_pMesh
);
머티리얼과 텍스쳐 로딩
- 머티리얼과 텍스쳐 정보를 x파일로부터 가져오기 위한 구조체
- 머티리얼 버퍼로부터 머티리얼과 텍서쳐 파일명을 가져오기 위해 사용한다.
typedef struct _D3DXMATERIAL
{
D3DMATERIAL9 MatD3D;
LPSTR pTextureFilename;
} D3DXMATERIAL;
typedef D3DXMATERIAL *LPD3DXMATERIAL;
x파일 로드 및 렌더링
//x파일로부터 데이터를 받을 변수들
LPD3DXMESH m_pMesh;//메쉬를 저장할 변수
D3DMATERIAL9 *m_pMeshMaterials;//머티리얼을 저장할 변수, 머티리얼은 여러개가 있을 수 있기 때문에 포인터 변수로 받는다.
LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9 *m_pMeshTextures;//텍스쳐 저장 변수
DWORD m_dwNumMaterials;//머티리얼의 개수
LPD3DXBUFFER pD3DXMtrlBuffer;//머티리얼 정보를 받아올 버퍼, 범용적인 데이터를 다룬는 객체이므로 형 변환이 필요하다.
//x파일 로드
D3DXLoadMeshFromX("../Resources/Meshes/Tiger/tiger.x",//x파일 경로
D3DXMESH_SYSTEMMEM, //메쉬 데이터를 생성할 메모리 지정, D3DXMESH_MANAGED, D3DXMESH_DYNAMIC
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice,//d3d 디바이스
nullptr,//인접 정점의 정보를 리턴, directx9에서는 사용하지 않는다.
&pD3DXMtrlBuffer,//머티리얼 정보를 리턴
nullptr,//effect의 초기값 리턴, directx9에서는 사용하지 않는다.
&m_dwNumMaterials,//머티리얼 개수 리턴
&m_pMesh //생성된 메쉬 객체를 리턴(정점 정보를 가진 버퍼)
);
//머티리얼 버퍼로부터 머티리얼을 가져올 수 있도록 시작 포인터를 얻는다.
D3DXMATERIAL *pD3dxMaterial = (D3DXMATERIAL *)pD3DXMtrlBuffer->GetBufferPointer();
//머티리얼을 저장 할 수 있도록 배열을 생성
m_pMeshMaterials = new D3DMATERIAL9[m_dwNumMaterials];
//텍스쳐를 저장 할 수 있도록 배열을 생성
m_pMeshTextures = new LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9[m_dwNumMaterials];//머티리얼 하나당 텍스쳐 하나(?)
//머티리얼 버퍼로부터 머티리얼을 저장
for (DWORD i = 0; i < m_dwNumMaterials; i++) {
//material
m_pMeshMaterials[i] = pD3dxMaterial[i].MatD3D;
m_pMeshMaterials[i].Ambient = m_pMeshMaterials[i].Diffuse;
//texture
m_pMeshTextures[i] = nullptr;
if (pD3dxMaterial[i].pTextureFilename != nullptr && strlen(pD3dxMaterial[i].pTextureFilename) > 0) {
//텍스쳐 생성
char szPath[MAX_PATH] = {};
sprintf_s(szPath, "../Resources/Meshes/Tiger/%s", pD3dxMaterial[i].pTextureFilename);
D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice, szPath, &m_pMeshTextures[i]);
}
}
//머티리얼 버퍼의 정보를 모두 저장했으므로 해제
pD3DXMtrlBuffer->Release();
pD3dxMaterial = nullptr;
//라이트 설정
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_LIGHTING, true);//메쉬에 정정 벡터가 있으므로 라이트를 켠다.
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_AMBIENT, 0xffffffff);//주변광을 백색으로 설정
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, true);//z버퍼를 켠다.
//렌더링
for (DWORD i = 0; i < m_dwNumMaterials; i++) {
//material
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetMaterial(&m_pMeshMaterials[i]);
//texture
pD3DFramework->pD3DDevice->SetTexture(0, m_pMeshTextures[i]);
//mesh
m_pMesh->DrawSubset(i);
}
Direct3D Framework
- Document
- DirectX Software Development Kit > Programming Guide > DXUT
DXUT 콜백 등록 함수
Direct3D device 관련 함수
DXUTSetCallbackDeviceCreated()
- 윈도우 초기화와 Direct3D device가 생성되었을 때 호출되는 함수를 설정
DXUTSetCallbackDeviceReset()
- Device의 소실 때 호출 함수 설정
DXUTSetCallbackDeviceLost()
- Direct3D device가 소실상태에 들어가면 호출되는 콜백함수를 설정
DXUTSetCallbackDeviceDestroyed()
- device를 재생성하거나 응용프로그램이 종료할 때 호출되는 콜백함수 설정
Frame 관련 함수
DXUTSetCallbackFrameMove()
- 프레임 갱신 시작 할 때 호출되는 콜백함수 설정
DXUTSetCallbackFrameRender()
- 화면에 출력하는 콜백함수를 설정
Msg 관련 함수
DXUTSetCallbackMsgProc()
- 윈도우 메시지가 발생될 때 호출되는 콜백함수를 설정
DXUTSetCallbackKeyboard()
- 키보드와 관련된 메시지가 발생될 때 호출되는 콜백함수를 설정
DXUTSetCallbackMouse()
- 마우스 메시지 발생될 때 호출되는 콜백함수를 설정
기타 함수
DXUTGetD3DDevice
- Direct3D 디바이스를 가져온다.
DXUTGetHWND()
- 현재 윈도우 핸들을 가져온다.
Direct3D Framework에서 실행되는 콜백 함수
OnD3D9CreateDevice()
- 특정한 d3d device에 대한 설정
- 백버퍼에 대한 설정
- 카메라와 프로젝션 설정
- d3d device에 한 번만 설정하는 코드
OnD3D9ResetDevice()
- device가 소실되었을 경우 device에 연관(연결)된 객체를 다시 셋업하기 위한 함수이다.
- 소실이란
- 화면에 보이는 윈도우가 가려지거나 크기 변경등이 일어났을 때 device에 설정한 객체(값)중 일부가 사라지는 것.
- 윈도우가 다시 화면에 나타날 때 소실된 객체를 다시 설정해줘야한다.
- 화면이 변경될 경우 백버퍼의 크기가 변경되므로 다시 설정해야한다.
OnFrameMove()
- 데이터 갱신 함수
OnD3D9FrameRender()
- 렌더링 함수
MsgProc()
- 응용프로그램의 윈도우 메시지를 처리
- WndProc()과 같은 역할
OnD3D9LostDevice()
- device에 연관된 객체를 해제
- OnD3D9ResetDevice()에서 생성된 객체를 해제
wWinMain()
- 어플리케이션의 시작점
콜백함수 호출 순서
- 윈도우 생성부터 종료 전까지
- IsD3D9DeviceAccepatble
- ModifyDeviceSettings
- OnD3D9CreateDevice
- OnD3D9ResetDevice
- OnD3D9FrameMove
- OnD3DFrameRender(->OnD3D9FrameMove 반복)
- 윈도우가 종료될 때
- OnD3D9LostDevice
- OnD3D9DestroyDevice
- Device 소실될 때 또는 윈도우 크기가 변경될 때
- OnD3D9LostDevice
- OnD3D9ResetDevice
윈도우와 Direct3D 생성 및 초기화
/*
HRESULT WINAPI DXUTInit( bool bParseCommandLine,
bool bShowMsgBoxOnError,
__in_opt WCHAR* strExtraCommandLineParams,
bool bThreadSafeDXUT )
*/
DXUTInit( true, true ); // Parse the command line and show error msgboxes
/*
void WINAPI DXUTSetHotkeyHandling( bool bAltEnterToToggleFullscreen, bool bEscapeToQuit, bool bPauseToToggleTimePause )
*/
DXUTSetHotkeyHandling( true, true, true ); // handle the default hotkeys
/*
void WINAPI DXUTSetCursorSettings( bool bShowCursorWhenFullScreen, bool bClipCursorWhenFullScreen )
*/
DXUTSetCursorSettings( true, true ); // Show the cursor and clip it when in full screen
/*
HRESULT WINAPI DXUTCreateWindow( const WCHAR* strWindowTitle, HINSTANCE hInstance,
HICON hIcon, HMENU hMenu, int x, int y )
*/
DXUTCreateWindow( L"EmptyProject" );
/*
HRESULT WINAPI DXUTCreateDevice( bool bWindowed, int nSuggestedWidth, int nSuggestedHeight )
*/
DXUTCreateDevice( true, 640, 480 );
게임 루프
DXUTMainLoop();
위 함수를 실행하면 다음 함수가 계속 실행된다.
MsgProc()
OnFrameMove()
OnD3D9FrameRender()
윈도우 모드와 전체화면 모드의 전환
DXUTToggleFullScreen()
위 함수가 실행되면 다음과 같은 흐름으로 전체화면 전환이 이루어진다.
- ModifyDeviceSettings()
- OnLostDevice()
- OnResetDevice()
- Toggle 실행
- OnFrameMove()
- OnFrameRender()
Direct3D Framework 기본 구조
EmptyProject
- Direct3D SDK가 제공하는 빈 프로젝트로써 가장 기본적인 Direct3D Framework의 구조를 볼 수 있다.
- DirectX Sample Browser를 통해 프로젝트를 생성할 수 있다.
//박스 메쉬를 그리는 예제
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// File: EmptyProject.cpp
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "DXUT.h"
#include "resource.h"
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Rejects any D3D9 devices that aren't acceptable to the app by returning false
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool CALLBACK IsD3D9DeviceAcceptable(D3DCAPS9* pCaps, D3DFORMAT AdapterFormat, D3DFORMAT BackBufferFormat,
bool bWindowed, void* pUserContext) {
// Typically want to skip back buffer formats that don't support alpha blending
IDirect3D9* pD3D = DXUTGetD3D9Object();
if (FAILED(pD3D->CheckDeviceFormat(pCaps->AdapterOrdinal, pCaps->DeviceType,
AdapterFormat, D3DUSAGE_QUERY_POSTPIXELSHADER_BLENDING,
D3DRTYPE_TEXTURE, BackBufferFormat)))
return false;
return true;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Before a device is created, modify the device settings as needed
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool CALLBACK ModifyDeviceSettings(DXUTDeviceSettings* pDeviceSettings, void* pUserContext) {
return true;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create any D3D9 resources that will live through a device reset (D3DPOOL_MANAGED)
// and aren't tied to the back buffer size
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LPD3DXMESH pMesh;
HRESULT CALLBACK OnD3D9CreateDevice(IDirect3DDevice9* pd3dDevice, const D3DSURFACE_DESC* pBackBufferSurfaceDesc,
void* pUserContext) {
//viewport
RECT sRect;
D3DVIEWPORT9 d3dViewport;
d3dViewport.X = 0;
d3dViewport.Y = 0;
d3dViewport.Width = pBackBufferSurfaceDesc->Width;
d3dViewport.Height = pBackBufferSurfaceDesc->Height;
d3dViewport.MinZ = 0.0f;
d3dViewport.MaxZ = 1.0f;
pd3dDevice->SetViewport(&d3dViewport);
//camera
D3DXMATRIX matCamera;
D3DXVECTOR3 vCameraEye = { 5.0f, 5.0f, -10.0f };
D3DXVECTOR3 vCameraAt = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f };
D3DXVECTOR3 vCameraUp = { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f };
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH(&matCamera, &vCameraEye, &vCameraAt, &vCameraUp);
pd3dDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_VIEW, &matCamera);
//projection
D3DXMATRIX matProj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(&matProj,
3.14*0.5,
pBackBufferSurfaceDesc->Width / pBackBufferSurfaceDesc->Height,
1.0f,
50.0f);
pd3dDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_PROJECTION, &matProj);
pd3dDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_FILLMODE, D3DFILL_WIREFRAME);
pd3dDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_LIGHTING, false);
pd3dDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, true);//z버퍼를 켠다.
//mesh
D3DXCreateBox(pd3dDevice, 1, 1, 1, &pMesh, nullptr);
return S_OK;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create any D3D9 resources that won't live through a device reset (D3DPOOL_DEFAULT)
// or that are tied to the back buffer size
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT CALLBACK OnD3D9ResetDevice(IDirect3DDevice9* pd3dDevice, const D3DSURFACE_DESC* pBackBufferSurfaceDesc,
void* pUserContext) {
return S_OK;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Handle updates to the scene. This is called regardless of which D3D API is used
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CALLBACK OnFrameMove(double fTime, float fElapsedTime, void* pUserContext) {
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Render the scene using the D3D9 device
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CALLBACK OnD3D9FrameRender(IDirect3DDevice9* pd3dDevice, double fTime, float fElapsedTime, void* pUserContext) {
HRESULT hr;
// Clear the render target and the zbuffer
V(pd3dDevice->Clear(0, NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER, D3DCOLOR_ARGB(0, 45, 50, 170), 1.0f, 0));
// Render the scene
if (SUCCEEDED(pd3dDevice->BeginScene())) {
//draw mesh
D3DXMATRIX matScale = {};
D3DXMATRIX matRot = {};
D3DXMATRIX matTranslate = {};
float fScale = 4.0f;
float fAngleY = 3.14*0.2;
D3DXMatrixScaling(&matScale, fScale, fScale, fScale);
D3DXMatrixRotationY(&matRot, fAngleY);
D3DXMatrixTranslation(&matTranslate, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
pd3dDevice->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &(matScale * matRot * matTranslate));
pMesh->DrawSubset(0);
V(pd3dDevice->EndScene());
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Handle messages to the application
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK MsgProc(HWND hWnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam,
bool* pbNoFurtherProcessing, void* pUserContext) {
return 0;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Release D3D9 resources created in the OnD3D9ResetDevice callback
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CALLBACK OnD3D9LostDevice(void* pUserContext) {
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Release D3D9 resources created in the OnD3D9CreateDevice callback
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CALLBACK OnD3D9DestroyDevice(void* pUserContext) {
if (pMesh) {
pMesh->Release();
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialize everything and go into a render loop
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE, HINSTANCE, LPWSTR, int) {
// Enable run-time memory check for debug builds.
#if defined(DEBUG) | defined(_DEBUG)
_CrtSetDbgFlag(_CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF | _CRTDBG_LEAK_CHECK_DF);
#endif
// Set the callback functions
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9DeviceAcceptable(IsD3D9DeviceAcceptable);
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9DeviceCreated(OnD3D9CreateDevice);
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9DeviceReset(OnD3D9ResetDevice);
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9FrameRender(OnD3D9FrameRender);
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9DeviceLost(OnD3D9LostDevice);
DXUTSetCallbackD3D9DeviceDestroyed(OnD3D9DestroyDevice);
DXUTSetCallbackDeviceChanging(ModifyDeviceSettings);
DXUTSetCallbackMsgProc(MsgProc);
DXUTSetCallbackFrameMove(OnFrameMove);
// TODO: Perform any application-level initialization here
// Initialize DXUT and create the desired Win32 window and Direct3D device for the application
DXUTInit(true, true); // Parse the command line and show msgboxes
DXUTSetHotkeyHandling(true, true, true); // handle the default hotkeys
DXUTSetCursorSettings(true, true); // Show the cursor and clip it when in full screen
DXUTCreateWindow(L"EmptyProject");
DXUTCreateDevice(true, 640, 480);
// Start the render loop
DXUTMainLoop();
// TODO: Perform any application-level cleanup here
return DXUTGetExitCode();
}
EmptyProject 프로젝트 실행 시 컴파일 에러 해결
- DXUTenum.cpp > 3375라인의 abs()함수를 fabsf()함수로 변경
- DXUT.h > 100라인쯤에 다음과 같은 코드 입력
- auto __vsnwprintf = _vsnwprintf;
DXUT 유틸리티 파일
DXUT.cpp
- Direct3D Framework 관련 대부분의 전역함수와 콜백함수들이 있다.
DXUTcamera.cpp
- 카메라 클래스가 있어서 툴과 게임에서 쉽게 카메라를 사용할 수 있게 해준다.
- 특히 CD3DArcBall 클래스는 툴을 만들 때 유용한 클래스이다.
DXUTenum.cpp
- Direct3D의 어뎁터와 디바이스와 모드에 대한 설정 함수가 있다.
DXUTgui.cpp
- Direct3D 다이얼로그, 리소스 관리자, 컨트롤(버튼, Static Text등)을 구현한 클래스가 있다.
DXUTmisc.cpp
- 타이머, 화면등에 관한 함수와 클래스가 있다.
- misc
- miscellaneous [mìsəléiniəs]
- 잡동사니, 여러가지, 기타, 갖가지의
DXUTres.cpp
- Direct3D에서 제공되는 리소스에 대한 아이디가 있다.
DXUTsettingsdlg.cpp
- Direct3D를 셋업하기 위한 Dialog GUI 클래스가 있다.
SDKmesh.cpp
- 메쉬를 다루기 위한 클래스가 있다.
SDKmisc.cpp
- 메쉬에 사용되는 텍스쳐와 텍스트 출력등에 관한 클래스가 있다.
Direct3D Sample Project
- 기본으로 유니코드 문자열을 사용하도록 설정되어있다.
- swprintf()
- %S 문자열을 유니코드로 변환
- %s 단일 문자를 유니코드로 변환
2D 이미지 출력
텍스쳐(이미지) 로딩
- D3DXCreateTextureFromFileEx()
- D3DXCreateTextureFromFile()의 확장형
- ColorKey -> D3DCOLOR_XRGB()
HRESULT D3DXCreateTextureFromFileEx(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice,//Direct3D 디바이스
LPCTSTR pSrcFile,//이미지 파일명
UINT Width,//이미지 세로 크기, 0 or D3DX_DEFAULT: 전체 이미지
UINT Height,//이미지 가로 크기, 0 or D3DX_DEFAULT: 전체 이미지
UINT MipLevels,//밉맵, 기본으로 0
DWORD Usage,//D3DUSAGE_RENDERTARGET 또는 D3DUSAGE_DYNAMIC, 기본 0
D3DFORMAT Format,//이미지 포맷, D3DFMT_UNKNOWN 의 경우, 포맷은 파일로부터 취득된다
D3DPOOL Pool,//텍스쳐가 배치될 메모리
DWORD Filter,//이미지를 필터링하는 방법을 제어, D3DX_DEFAULT == D3DX_FILTER_TRIANGLE | D3DX_FILTER_DITHER
DWORD MipFilter,//이미지를 필터링하는 방법을 제어, D3DX_DEFAULT == D3DX_FILTER_BOX
D3DCOLOR ColorKey,//투명이될 컬러, D3DCOLOR_XRGB()로 지정할 수 있고 0이라면 컬러키가 없다. 알파값이 유효하다
D3DXIMAGE_INFO *pSrcInfo,//nullptr
PALETTEENTRY *pPalette,//nullptr
LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9 *ppTexture//텍스쳐를 사용할 포인터 변수의 포인터
);
ID3DXSprite를 이용한 텍스쳐 출력
- 2D 스프라이트 출력
- 게임 UI에 많이 사용
- d3dx9core.h, d3dx9.lib
- 출력 시작과 종료
- 텍스쳐는 원본 그림이고 스프라이트는 이를 사용하기 좋게 감싸는 클래스라 생각하면 된다.
//ID3DXSprite생성
HRESULT D3DXCreateSprite(
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 pDevice,
LPD3DXSPRITE *ppSprite
);
//ID3DXSprite 해제
ID3DXSprite::Release()
//출력 시작
//IDirect3DDevice9::BeginScene 와 IDirect3DDevice9::EndScene 의 순서의 안쪽에서 호출해야한다.
HRESULT ID3DXSprite::Begin(
[in] DWORD Flags//스프라이트 렌더링 옵션, D3DXSPRITE_...
);
//출력
//Begin()과 End() 안쪽에서 호출
HRESULT ID3DXSprite::Draw(
[in] LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9 pTexture,//텍스쳐 객체의 포인터
[in] const RECT *pSrcRect,//텍스쳐의 출력 영역
[in] const D3DXVECTOR3 *pCenter,//스프라이트의 출력 기준점, 좌상단이 (0,0)
[in] const D3DXVECTOR3 *pPosition,//스프라이트 출력 위치
[in] D3DCOLOR Color//텍스쳐의 컬러값을 변경(알파 블렌딩), 0xFFFFFFFF는 원본색상을 유지, D3DCOLOR_XRGB() 사용
);
//출력 종료
//ID3DXSprite::Flush를 호출하고 디바이스의 상태를 ID3DXSprite::Begin()호출 이전으로 돌린다.
//ID3DXSprite::Flush는 지금까지 배치된 스프라이트를 디바이스로 보내서 그리게하고 배치 스프라이트 리스트를 비운다.
HRESULT ID3DXSprite::End();
키보드 처리
-
Win32 API
- GetAsyncKeyState() 함수 사용
- Update
-
Direct3D
-
DXUT 함수 사용
- DXUTIsKeyDown() -> 가상 키로 체크
- 요즘은 컨트롤러를 지원하지 않는다면 굳이 DirectInput을 사용하지 않아도 된다고 한다.
- 속도상 이점이 전혀 없기 때문
- 컨트롤러 또는 XBox를 지원하기 위해서는 XInput을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 따라서 간단한 프로젝트는 Win32의 GetAsyncKeyState를 사용해도 된다.
-
마우스 처리
- Win32 API
- 마우스 관련 메시지 사용
- WM_LBUTTONDOWN, …, WM_MOUSEMOVE, …
- Direct3D
- DXUT 프레임워크를 사용한다면 마우스 관련 콜백함수를 사용
- Win32 API와 같은 메시지가 넘어오므로 Win32 API와 로직은 같다
- DXUT 프레임워크를 사용한다면 마우스 관련 콜백함수를 사용
영어
- reciprocal [risíprəkəl]
- 상호의, 상응하는
- homogeneous [hòumədʒíːniəs]
- 동종의, 순일의, 동원의
- strip
- 스트립, 띠, 박탈하다, 벗기다, 박판
- translation
- 평행 이동
- transformation
- 변형, 변환
- adjacency [ədʒéisnsi]
- 인접, 근접
- stride [straid]
- 보폭, 발전, 진전, 성큼성큼, 활보
참고
- https://abipictures.tistory.com/115
- https://vallista.tistory.com/entry/DX-9-Direct3D-%EC%8B%9C%EC%9E%91
- DirectX 3D 게임 프로그래밍
- 정점 포맷과 정점 버퍼
- Working with D3DXMath
- https://stonzeteam.github.io/SIMD-%EB%B3%91%EB%A0%AC-%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9C%EA%B7%B8%EB%9E%98%EB%B0%8D/
- http://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=qkfdjq451&logNo=220842864791&beginTime=0&jumpingVid=&from=search&redirect=Log&widgetTypeCall=true
- DrawIndexedPrimitive() 함수에 대하여 조금 상세히..
- 행/열기준 행렬 및 OpenGL 성능
- D3DXVec3Transform 세가지 함수
- 나우캠퍼스 3D 게임 프로그래밍
- DXUT 사용하는 방법